 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
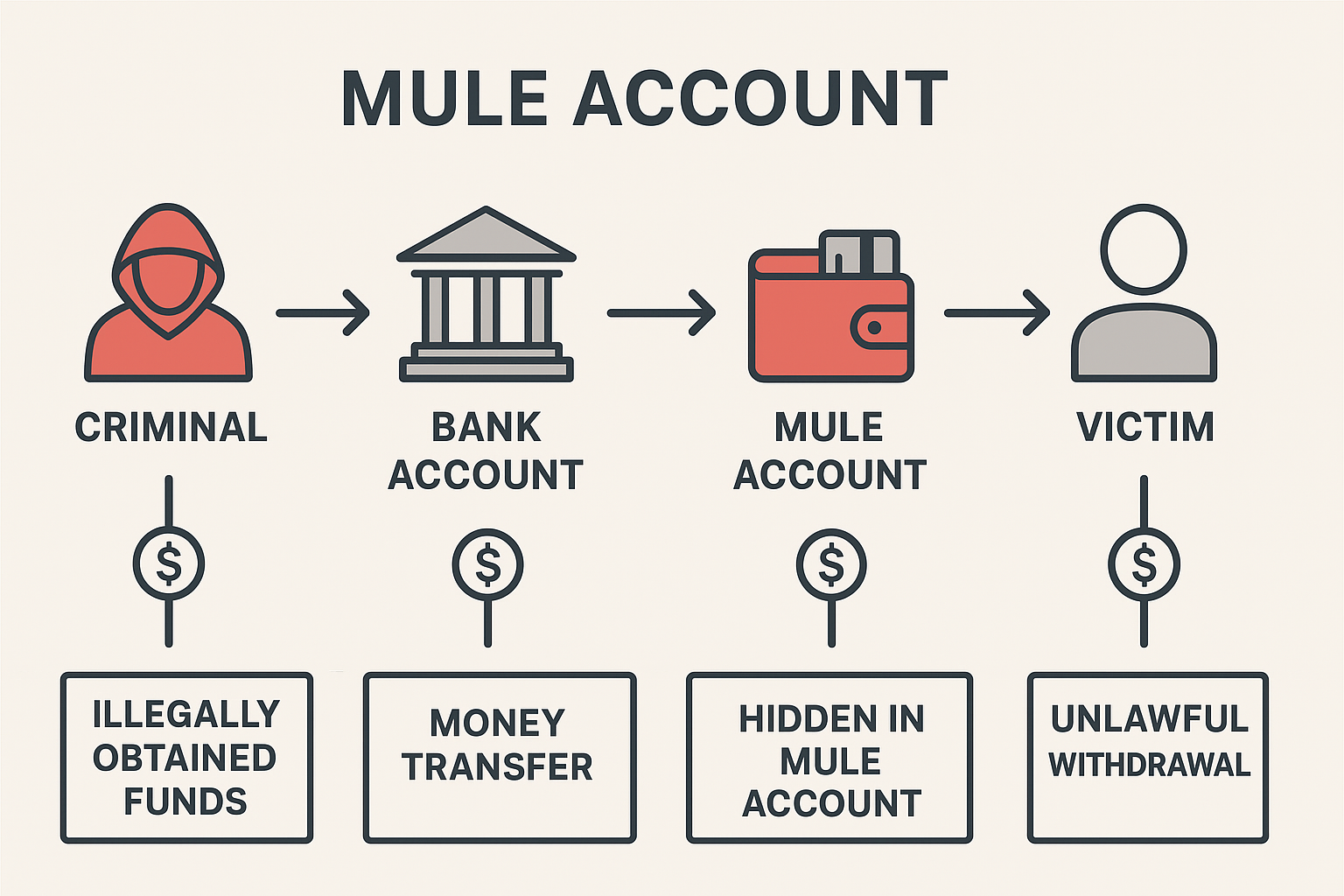
A Mule Account, Often Called A Money mule Account, Is A Bank Account Used—knowingly Or Unknowingly—to Receive, Transfer, Or Withdraw Illegally Obtained Money On Behalf Of Criminals. In The Global Financial Crime Ecosystem, Mule Accounts Are A Crucial Layer Of Obfuscation.
They Help Criminals Hide Their Identity, Mask The Origin Of Stolen Or Fraudulently Obtained Funds, And Complicate The Tracing Process For Investigators. Increasingly, Digital Payment Systems, Social Media Scams, And International Fraud Rings Have Boosted The Scale And Sophistication Of Mule-account Operations.
In Legitimate Financial Systems, Every Bank Transfer Creates A Traceable Record. Criminals Attempt To Break This Traceability By Using Large Networks Of Intermediaries—ordinary People Or Stolen Identities—whose Accounts Act As Temporary Holding Stations. These Individuals, The “money Mules,” Serve To distance The Main Criminals From The Crime. Because Of This, Law Enforcement Agencies Worldwide Treat Mule Accounts As Essential Leads In Larger Investigations Into Fraud, Cybercrime, Money Laundering, Trafficking, Or Illicit Online Businesses.
But Many People Still Do Not Fully Understand What A Mule Account Is, How Criminals Recruit Mules, Or The Severe Consequences—even For Those Who Participate Unknowingly. This Article Explains Everything In Detail.
A mule Account Refers To:
that Criminals Use To store, Move, Or Withdraw illegal Funds.
The Person Who Provides Or Controls The Account Is The **money Mule**, And They May Act:
1. Knowingly (actively Participating In Crime For Financial Gain)
2. Unknowingly (tricked Into Believing It Is A Legitimate Job Or Request)
3. By Coercion (forced Or Threatened To Give Access)
The Account Becomes A buffer between The Original Source Of Money (the Victim) And The Mastermind (the Criminal). This “layering” Helps Criminals Disguise The Money Trail.
Criminals Rely Heavily On Mule Accounts For Several Reasons:
a. To Avoid Detection
Money Moving Directly From A Fraudster’s Account To Their Own Is Easily Traceable. Mule Accounts Create Multiple Layers Of Transfers To Confuse Investigators.
b. To Add Distance From The Crime
When Investigators Follow The Money, The Trail Leads To The Mule, Not The Real Criminal.
c. To Exploit Weak KYC
In Many Countries, Criminals Gather:
and Convert Them Into Mule Accounts To Bypass Strict Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations.
d. To Enable Large-Scale Operations
Online Scams Like Phishing, Sextortion, Job Scams, Investment Fraud, Or Romance Scams Generate thousands Of Micro-transactions. Mule Accounts Are Essential To Collect And Consolidate These Funds.
e. To Launder Money
Mule Accounts Help Convert “dirty” Money (from Illegal Activities) Into “clean” Money By Passing It Through Many Accounts—a Process Called money Laundering.
A Mule Account Usually Has One Or More Of The Following Traits:
These Patterns Are Red Flags For Banks.
Money-mule Activities Fall Into Three Primary Categories:
a. Innocent / Unwitting Money Mule
These Individuals Do Not Realize They Are Participating In A Crime.
Examples:
They Believe It Is Legitimate Work, But It Is Actually Criminal Activity.
b. Witting Money Mule
These People Suspect The Activity Is Illegal But Proceed Because Of Financial Benefit.
Signs:
They Know Something Is Wrong But Continue Willingly.
c. Complicit / Criminal Money Mule
These Individuals Knowingly Collaborate With Fraudsters.
They May:
This Category Is Treated As A Serious Criminal Offense.
a. Fake Job Offers
Scammers Advertise Positions Like:
These Ads Pay Unusually High Salaries For Simple Tasks.
b. Social Media Or Messaging Apps
Platforms Like WhatsApp, Telegram, Instagram, And Facebook Are Used To Recruit Young People.
c. Romance And Online Friendship Scams
Victims Are Emotionally Manipulated To “help Me Receive Money” Or “pay My Business Associate.”
d. Student Recruitment
Criminals Target Students, Claiming They Can Earn “easy Passive Income.”
e. Selling Or Renting Bank Accounts
Some Criminals Approach Poor Individuals And Offer Money In Exchange For Access To Their Accounts.
f. Fake Loan Apps
Fraudulent Loan Providers Demand “bank Verification” And Later Misuse The Account.
Money Laundering Through Mule Accounts Often Follows The Classical three-step Model:
Stage 1: Placement
Illegal Money Enters The Financial System.
This Money Is Deposited Into Mule Accounts.
Stage 2: Layering
Funds Are Split And Moved Rapidly Between Multiple Mule Accounts To Hide Their Origin.
This Phase Creates Confusion And Distance For Investigators.
Stage 3: Integration
Finally, Criminals Withdraw Or Use The Cleaned Money:
At This Point, The Funds Appear “legitimate.”
Criminal Groups Use A Variety Of Techniques:
a. Remote Access Tools
Apps Like:
allow Criminals To Control The Mule’s Device And Initiate Transactions.
b. SIM Swapping
They Take Control Of The Mule’s Phone Number To Bypass OTP Verification.
c. Fake KYC Documents
To Create New Accounts Using Stolen Identities.
d. Crypto Anonymizers
Used To Obscure Digital Transactions.
e. Mixing Services
To Blend Illegal Crypto Funds With Legitimate Ones.
f. Fraudulent Payment Gateways
To Create Fake Businesses And Divert Customer Payments.
Banks And Government Agencies Use:
a. Transaction Monitoring Systems (TMS)
AI-based Systems Detect Suspicious Patterns Such As:
b. Suspicious Transaction Reports (STR)
Banks File Alerts To Financial Regulators.
c. KYC And CKYC Databases
To Check Document Authenticity.
d. Account Freezing
If Suspicious Activity Is Detected, The Bank Can Freeze The Account Instantly.
e. IP Address And Device Tracking
Authorities Check:
f. Money Trail Forensics
Investigators Reconstruct Transactions Through The Banking System.
g. Cross-border Cooperation
Multiple Countries Share Intelligence Through:
a. Online Job Scam
A Person Receives A Message Claiming To Offer Flexible Online Work. They Are Told:
1. Receive Funds
2. Withdraw Them
3. Send To Another Account Via UPI Or Crypto
This Is A Classic Mule-operation Workflow.
b. Investment Fraud
Victims Deposit Money Into A Mule Account Belonging To Someone Recruited By The Fraudsters.
c. Cybercrime Syndicates
Large Networks Create Hundreds Of Mule Accounts Using Fake Identities.
d. Romance Scams
Victims Unknowingly Help Transfer Illegal Money For Someone They Think They Are Dating.
Even If Someone Participates Unknowingly, They Face:
A. Legal Consequences
Possible Charges Include:
Punishments May Include:
B. Financial Consequences
C. Cybersecurity Risks
D. Reputational Consequences
Be Cautious If You Encounter:
a. Never Share Bank Login Credentials
No Employer Or Legitimate Business Needs Your Net Banking Or UPI Access.
b. Do Not Receive Money From Unknown Sources
If You Cannot Explain Why Money Entered Your Account, You Are At Risk.
c. Verify Jobs Before Applying
Especially Those Offering High Pay For Simple Tasks.
d. Do Not Allow Others To Use Your Bank Account
Even Family Members Should Use Their Own Accounts.
e. Report Suspicious Transactions Immediately
Banks And Cybercrime Portals Can Help You.
f. Avoid Installing Remote-access Apps
Unless You Trust The Source Completely.
1. Immediately Contact Your Bank And Request An Account Freeze.
2. Change All Passwords, UPI PINs, And Remove Suspicious Devices.
3. File A Report On Your Country’s Cybercrime Portal (e.g., India: Cybercrime.gov.in).
4. Keep A Record Of All Communication With The Scammer.
5. Consult A Legal Advisor If Needed.
6. Inform The Police If The Activity Involves Large Sums.
Mule Accounts Are A Fundamental Part Of Modern Financial Crime. From Phishing Scams To International Money Laundering Operations, Criminals Rely On These Accounts To Hide Their Identity And Move Illegal Money Across Borders. Unfortunately, Many Ordinary People Become Unwitting Mules Through Fake Job Scams, Social Engineering, Or Online Manipulation. Once Their Account Is Used For Fraud Or Money Laundering, They Face Severe Legal And Financial Consequences—even If They Were Unaware Of The Crime.
Understanding How Mule Accounts Work Is Essential For Protecting Yourself And Your Community. Always Be Cautious About Sharing Bank Information, Avoid Suspicious Job Offers, And Stay Alert To Unexpected Deposits. With Financial Fraud Growing Rapidly In The Digital Age, Awareness Is The First Line Of Defense.
Mule Account, What Is Mule Account, Define Mule Account