 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
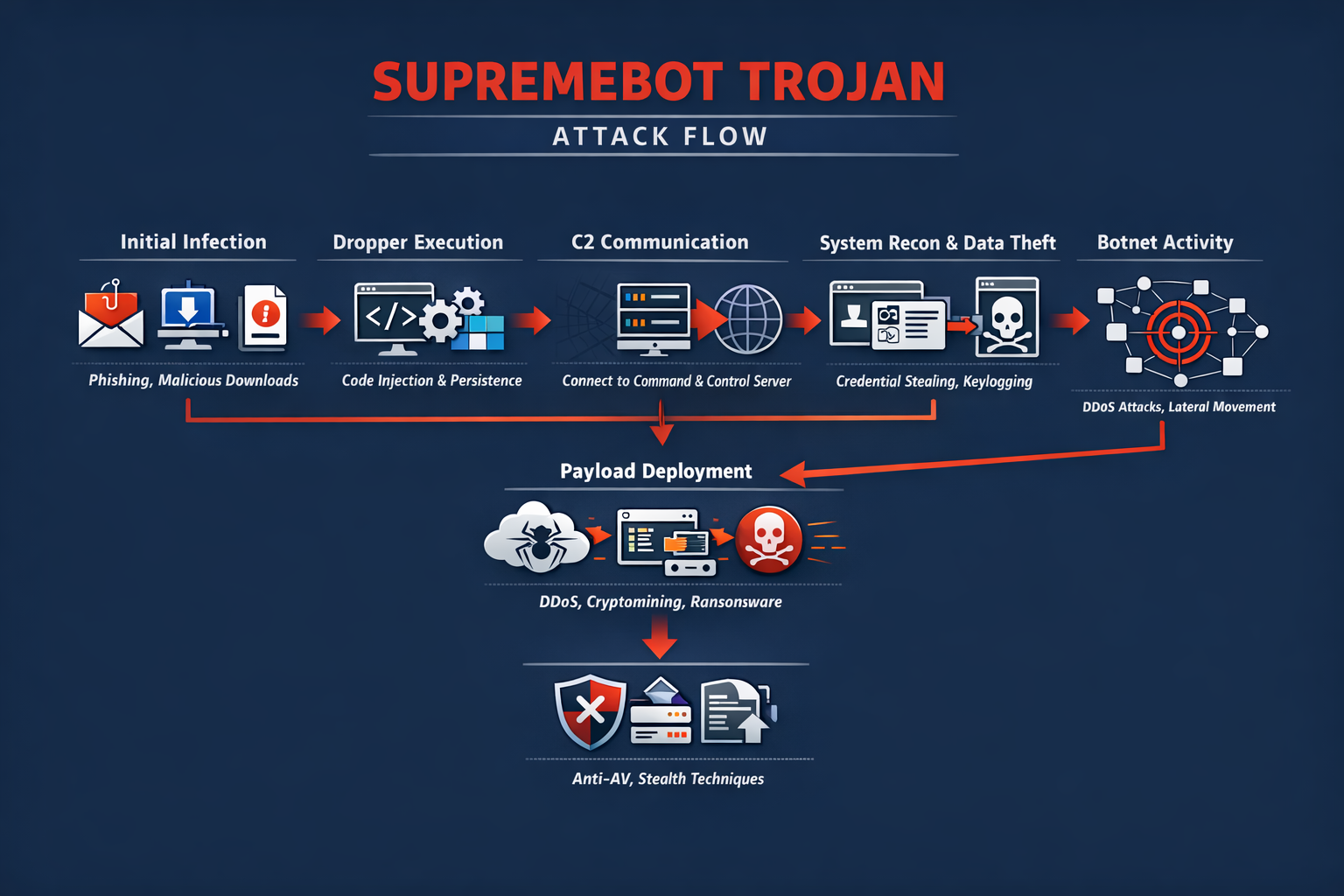
The SupremeBot Trojan Is An Emerging And Highly Adaptable Malware Strain That Belongs To The Broader Category Of Remote Access Trojans (RATs) And Botnet Malware. Designed To Silently Infiltrate Systems And Establish Persistent Control, SupremeBot Enables Threat Actors To Execute Commands Remotely, Deploy Additional Payloads, Harvest Sensitive Data, And Integrate Infected Machines Into Coordinated Botnet Infrastructures.
With Cybercriminal Operations Increasingly Shifting Toward Malware-as-a-service (MaaS) Ecosystems, SupremeBot Is Frequently Marketed And Distributed Through Underground Forums, Making It Accessible Even To Low-skill Attackers. This Accessibility, Combined With Advanced Evasion And Persistence Techniques, Makes SupremeBot A Growing Threat To Individuals, Enterprises, And Critical Infrastructure.

From A Technical Perspective, SupremeBot Demonstrates Modular Architecture, Allowing Operators To Enable Or Disable Functionalities Depending On Campaign Objectives. This Flexibility Supports Various Malicious Use Cases Including Credential Theft, Distributed Denial-of-service (DDoS) Attacks, Cryptomining, Spyware Deployment, And Ransomware Delivery.
SupremeBot Infections Are Often Part Of Multi-stage Attack Chains Where Initial Compromise Occurs Via Phishing Or Exploit Kits, Followed By Silent Deployment Of The Trojan That Acts As A Command Hub For Further Actions. Because Of Its Stealthy Execution And Encrypted Communications, Many Victims Remain Unaware Of The Compromise For Extended Periods.
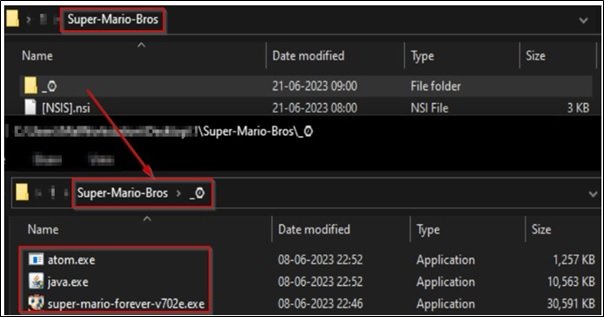
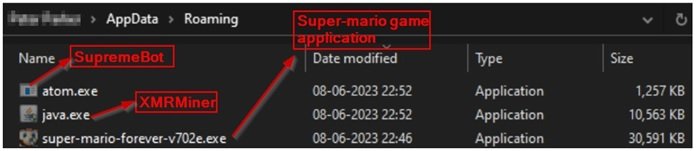
SupremeBot Typically Enters Systems Through Socially Engineered Lures Such As Fake Software Cracks, Pirated Games, Email Attachments, Malicious Advertisements, And Trojanized Installers. In Many Cases, Users Unknowingly Download The Malware While Attempting To Install Free Utilities Or Browser Extensions From Untrusted Sources.
Once Executed, The Dropper Component Injects Malicious Code Into Legitimate Processes To Avoid Detection, Modifies Registry Entries For Persistence, And Establishes Outbound Connections To Command-and-control (C2) Servers Hosted On Compromised Infrastructure Or Bulletproof Hosting Services. This Covert Communication Channel Allows Attackers To Maintain Continuous Remote Control Over Infected Endpoints.
A Defining Feature Of SupremeBot Is Its Robust Persistence Mechanisms. The Trojan Modifies Windows Startup Entries, Scheduled Tasks, And Registry Run Keys To Ensure Automatic Execution Upon Reboot. Some Variants Also Leverage Fileless Techniques By Storing Payloads In Memory And Invoking Them Through PowerShell Or Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), Making Forensic Detection More Difficult.
Additionally, SupremeBot May Disable Windows Defender Components, Terminate Security Services, And Add Exclusions To Antivirus Configurations To Maintain Long-term Foothold On Compromised Systems. These Persistence Tactics Significantly Increase Dwell Time, Allowing Attackers To Conduct Extended Surveillance And Exploitation.
Once Active, SupremeBot Collects Extensive System Information Including Operating System Version, Hardware Configuration, Network Identifiers, Installed Applications, Browser Data, And Security Software Presence. This Reconnaissance Phase Allows Attackers To Profile Victims And Tailor Subsequent Payloads Accordingly.
In Enterprise Environments, This Data Is Valuable For Identifying Lateral Movement Opportunities And Targeting High-value Systems Such As Database Servers Or Domain Controllers. The Stolen Information Is Transmitted To C2 Servers Using Encrypted HTTP Or Custom TCP Protocols To Evade Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems.
One Of The Primary Operational Goals Of SupremeBot Is Credential Harvesting. The Malware Integrates Browser Data Extraction Modules Capable Of Stealing Saved Passwords, Cookies, Autofill Data, And Cryptocurrency Wallet Credentials. Some Versions Also Include Keylogging Functionality That Records Keystrokes And Screenshots, Enabling Attackers To Capture Banking Logins, Corporate VPN Credentials, And Cloud Service Access Tokens. With These Stolen Credentials, Attackers Can Conduct Identity Theft, Financial Fraud, And Unauthorized Access To Corporate Resources, Often Escalating Attacks Into Full-scale Breaches.
SupremeBot Is Also Widely Used As A Botnet Agent For DDoS Attacks. Infected Systems Can Be Instructed To Flood Target Servers With Massive Volumes Of Network Traffic, Disrupting Online Services And Causing Financial Losses. These DDoS Capabilities Are Often Rented Out To Criminal Customers Seeking To Attack Competitors, Gaming Platforms, Or Political Targets. Because Botnets Are Composed Of Geographically Distributed Endpoints, Attribution And Mitigation Become Challenging, Making SupremeBot A Valuable Asset In Cyber Extortion Campaigns And Hacktivist Operations.
Another Monetization Strategy Involves Deploying Cryptomining Modules That Hijack CPU And GPU Resources To Mine Cryptocurrencies Such As Monero. This Silent Cryptojacking Leads To Significant Performance Degradation, Increased Power Consumption, And Hardware Wear. In Corporate Environments, Cryptomining Infections Can Result In Substantial Infrastructure Costs And Operational Disruptions. SupremeBot Dynamically Adjusts Mining Intensity To Avoid Detection By Performance Monitoring Tools, Further Prolonging Infection Duration.
In Many Attack Scenarios, SupremeBot Acts As An Initial Access Broker For More Destructive Payloads Such As Ransomware. Once Attackers Confirm Valuable Data Presence And Network Connectivity, They May Deploy Ransomware Families That Encrypt Files And Demand Ransom Payments. This Staged Attack Model Increases Success Rates By Ensuring That Ransomware Is Delivered Only After Reconnaissance Confirms Maximum Impact Potential. Consequently, SupremeBot Is Often Linked To Ransomware-as-a-service Affiliates Who Rely On Trojan Infections To Gain Entry Into Victim Networks.
To Evade Detection, SupremeBot Employs Multiple Obfuscation And Anti-analysis Techniques. Code Packing, String Encryption, API Hashing, And Dynamic Payload Loading Make Static Analysis Difficult. Some Variants Include Sandbox Detection Logic That Delays Execution If Virtualized Environments Are Detected, Preventing Automated Malware Scanners From Capturing Full Behavioral Profiles. Additionally, Polymorphic Updates Allow The Malware To Frequently Change File Signatures, Reducing Detection Rates By Signature-based Antivirus Engines.
Network Communication Is Another Area Where SupremeBot Demonstrates Sophistication. C2 Servers Are Often Rotated Using Fast-flux DNS Techniques Or Domain Generation Algorithms (DGAs), Making Takedown Efforts Complex. Encrypted Traffic Blends Into Legitimate Web Traffic, Bypassing Traditional Firewall Rules. Some Campaigns Even Leverage Popular Cloud Services As Relay Nodes, Exploiting Trusted Platforms To Mask Malicious Data Exfiltration. These Tactics Significantly Complicate Network-level Detection And Incident Response.
The Impact Of SupremeBot Infections Extends Beyond Individual Devices. In Organizational Settings, Compromised Machines Can Be Leveraged For Internal Reconnaissance, Credential Dumping, And Lateral Movement Using Tools Such As Mimikatz-style Modules. This Enables Attackers To Pivot Across Networks, Compromise Additional Systems, And Escalate Privileges To Domain Administrator Levels. Ultimately, What Begins As A Single Trojan Infection Can Evolve Into Full Network Compromise, Data Exfiltration, Regulatory Penalties, And Reputational Damage.
Detecting SupremeBot Requires Multi-layered Security Strategies Combining Endpoint Detection And Response (EDR), Network Traffic Analysis, And Behavioral Monitoring. Indicators Of Compromise May Include Unusual Outbound Connections, Unauthorized Scheduled Tasks, Suspicious Registry Modifications, And Unexplained CPU Spikes. However, Due To Stealth Techniques, Traditional Antivirus Solutions May Fail To Detect Infections Until Damage Has Already Occurred. Therefore, Behavioral-based Threat Detection Platforms Play A Crucial Role In Identifying Anomalous Activity Patterns Associated With Botnet Communication And Credential Theft.
Manual Removal Of SupremeBot Is Complex And Risky Due To Hidden Persistence Hooks And Fileless Execution Methods. Simply Deleting Visible Files Often Fails To Eliminate The Infection Completely, As Scheduled Tasks, Registry Keys, And Memory-resident Components May Reinstate Malware Upon Reboot. Comprehensive Malware Removal Requires Full System Scans, Restoration Of Security Configurations, Termination Of Malicious Processes, And Validation Of Startup Entries. In Enterprise Incidents, Full System Reimaging Is Often Recommended To Ensure Complete Eradication.
Preventing SupremeBot Infections Starts With Strong Cybersecurity Hygiene Practices. Users Should Avoid Downloading Cracked Software, Pirated Content, And Unknown Email Attachments. Application Whitelisting, Patch Management, And Least-privilege User Policies Significantly Reduce Exploitation Risks. Regular Operating System And Browser Updates Close Vulnerabilities Commonly Exploited By Malware Droppers. In Addition, Network Segmentation Limits Lateral Movement Opportunities If An Endpoint Becomes Compromised.
Employee Cybersecurity Awareness Training Is Critical, Especially In Corporate Environments Where Phishing Remains A Primary Delivery Mechanism. Simulated Phishing Campaigns And Continuous Education Programs Help Reduce Click-through Rates On Malicious Links And Attachments. Since SupremeBot Frequently Arrives Through Social Engineering Tactics, Informed Users Become A Strong First Line Of Defense. Moreover, Email Gateway Filtering And Attachment Sandboxing Technologies Can Block Malware Before It Reaches Endpoints.
From An Organizational Risk Management Perspective, Incident Response Planning Is Essential For Containing Trojan Outbreaks. Clear Procedures For Isolating Infected Systems, Revoking Compromised Credentials, And Restoring Backups Can Drastically Reduce Damage. Logging And Forensic Analysis Support Root-cause Investigations, Helping Security Teams Identify Initial Infection Vectors And Strengthen Defenses Against Future Campaigns. Collaboration With Threat Intelligence Providers Also Enables Proactive Blocking Of Known Malicious Infrastructure Associated With SupremeBot Campaigns.
The Rise Of SupremeBot Reflects Broader Trends In Cybercrime Commercialization. Malware Developers Increasingly Sell Turnkey Botnet Kits, Updates, And Technical Support, Allowing Criminal Operators To Launch Campaigns Without Deep Technical Knowledge. This Democratization Of Cybercrime Fuels Rapid Malware Proliferation And Makes Takedown Efforts More Difficult. As Long As Underground Marketplaces Remain Profitable, Malware Families Like SupremeBot Will Continue Evolving With New Capabilities And Evasion Strategies.
In Academic And Research Contexts, SupremeBot Provides A Relevant Case Study For Understanding Modern Botnet Architectures, Modular Malware Design, And Hybrid Monetization Strategies. Its Combination Of Credential Theft, DDoS, Cryptomining, And Ransomware Delivery Illustrates How Contemporary Malware Ecosystems Integrate Multiple Revenue Streams Within A Single Framework. For Cybersecurity Students And Professionals, Analyzing Such Malware Highlights The Importance Of Layered Defenses, Behavioral Analytics, And Rapid Response Mechanisms.
In Conclusion, The SupremeBot Trojan Represents A Significant And Evolving Cybersecurity Threat Characterized By Stealth, Flexibility, And Multi-purpose Exploitation Capabilities. Its Ability To Function As A Botnet Agent, Spyware Platform, Cryptominer, And Ransomware Loader Makes It A Powerful Tool In Criminal Arsenals.
With Infections Often Remaining Undetected For Long Periods, Victims Face Serious Risks Including Financial Theft, Identity Compromise, And Full Network Breaches. Combating SupremeBot Requires Proactive Security Measures, Continuous Monitoring, And Strong User Awareness To Prevent Initial Infection And Detect Malicious Behavior Early. As Cybercriminal Techniques Grow Increasingly Sophisticated, Only Adaptive And Intelligence-driven Security Strategies Can Effectively Mitigate Threats Posed By Advanced Trojan Families Like SupremeBot.
Step 1: Boot Into Safe Mode
Restart Your PC And Press F8 (or Shift + F8 For Some Systems) Before Windows Loads.
Choose Safe Mode With Networking.
Safe Mode Prevents Most Malware From Loading.
Press Win + R, Type appwiz.cpl, And Press Enter.
Sort By Install Date And Uninstall Unknown Or Recently Added Programs.
Use A Trusted Anti-malware Tool:
Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com
Screenshot Of Malwarebytes - Visit Links
Microsoft Defender – Built Into Windows 10/11
HitmanPro, ESET Online Scanner, Or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
VIPRE Antivirus - US And Others Countries, | India
Run A Full Scan And Delete/quarantine Detected Threats.
Win + R, Type temp → Delete All Files.Press Win + R, Type %temp% → Delete All Files.
Use Disk Cleanup: cleanmgr In The Run Dialog.
Go To: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Open hosts File With Notepad.
Replace With Default Content:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Open Task Manager
Go To Startup Tab
Disable Any Suspicious Entries.
Open Command Prompt As Administrator.
Run These Commands:
netsh Winsock Reset
netsh Int Ip Reset
ipconfig /flushdns
Unwanted Homepage Or Search Engine
Pop-ups Or Redirects
Unknown Extensions Installed
For Chrome:
Go To: chrome://extensions/
Remove Anything Unfamiliar
For Firefox:
Go To: about:addons → Extensions
Remove Suspicious Add-ons
For Edge:
Go To: edge://extensions/
Uninstall Unknown Add-ons
Chrome:
Go To chrome://settings/reset → "Restore Settings To Their Original Defaults"
Firefox:
Go To about:support → "Refresh Firefox"
Edge:
Go To edge://settings/resetProfileSettings → "Reset Settings"
All Browsers:
Use Ctrl + Shift + Del → Select All Time
Clear Cookies, Cached Files, And Site Data
Make Sure They Are Not Hijacked.
Chrome: chrome://settings/search
Firefox: about:preferences#search
Edge: edge://settings/search
Chrome: chrome://settings/cleanup
Use Malwarebytes Browser Guard For Real-time Browser Protection.
Always Download Software From Trusted Sources.
Keep Windows, Browsers, And Antivirus Updated.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links Or Ads.
Use ad Blockers And reputable Antivirus Software.
Backup Your Files Regularly.
To Remove Malware From Your Windows PC, Start By Booting Into Safe Mode, Uninstalling Suspicious Programs, And Scanning With Trusted Anti-malware Tools Like Malwarebytes. Clear Temporary Files, Reset Your Network Settings, And Check Startup Apps For Anything Unusual.
For web Browsers, Remove Unwanted Extensions, Reset Browser Settings, Clear Cache And Cookies, And Ensure Your Homepage And Search Engine Haven’t Been Hijacked. Use Cleanup Tools Like Chrome Cleanup Or Browser Guard For Added Protection.
?? Prevention Tips: Keep Software Updated, Avoid Suspicious Downloads, And Use Antivirus Protection Plus Browser Ad Blockers. Regular Backups Are Essential.
Why It Matters: Not All VPNs Offer Malware Protection.
What To Look For: Providers With built-in Malware/ad/tracker Blockers (e.g., NordVPN’s Threat Protection, ProtonVPN’s NetShield).
Purpose: Prevents Data Leaks If Your VPN Connection Drops.
Benefit: Ensures Your Real IP And Browsing Activity Aren’t Exposed To Malware-distributing Websites.
Why It Matters: DNS Leaks Can Expose Your Online Activity To Attackers.
Solution: Enable DNS Leak Protection In Your VPN Settings Or Use A Secure DNS Like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Risk: Free VPNs Often Contain Malware, Sell User Data, Or Lack Security Features.
Better Option: Use Reputable Paid VPNs That Offer security Audits And Transparent Privacy Policies.
Some VPNs Block Known Phishing And Malicious Sites.
Example: Surfshark’s CleanWeb, CyberGhost’s Content Blocker.
Reason: Security Patches Fix Known Vulnerabilities.
Tip: Enable Auto-updates Or Check For Updates Weekly.
Scope: Malware Can Enter Through Phones, Tablets, Or IoT Devices.
Solution: Install VPN Apps On Every Internet-connected Device.
Fact: VPNs Do Not Remove Or Detect Malware On Your System.
Complement It With:
Antivirus Software
Firewall
Browser Extensions For Script Blocking
VPN Encrypts Traffic But Can’t Stop Malware From Executing If You Download Infected Files.
Split Tunneling Allows Certain Apps/sites To Bypass VPN.
Tip: Never Exclude Browsers, Email Clients, Or Download Managers From VPN Tunneling.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) Enhances Your Online Privacy By Encrypting Your Internet Traffic And Masking Your IP Address. It Protects Your Data On Public Wi-Fi, Hides Browsing Activity From Hackers And ISPs, And Helps Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs Also Add A Layer Of Defense Against Malware By Blocking Malicious Websites And Trackers When Using Advanced Features. However, A VPN Does Not Remove Existing Malware Or Act As Antivirus Software. For Full Protection, Combine VPN Use With Antivirus Tools, Regular Software Updates, And Cautious Browsing Habits. Always Choose A Reputable VPN Provider With Strong Security And Privacy Policies.
SupremeBot Trojan, Remove SupremeBot Trojan, Uninstall SupremeBot Trojan, Get Rid Of SupremeBot Trojan, SupremeBot Trojan Removal Guide