 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
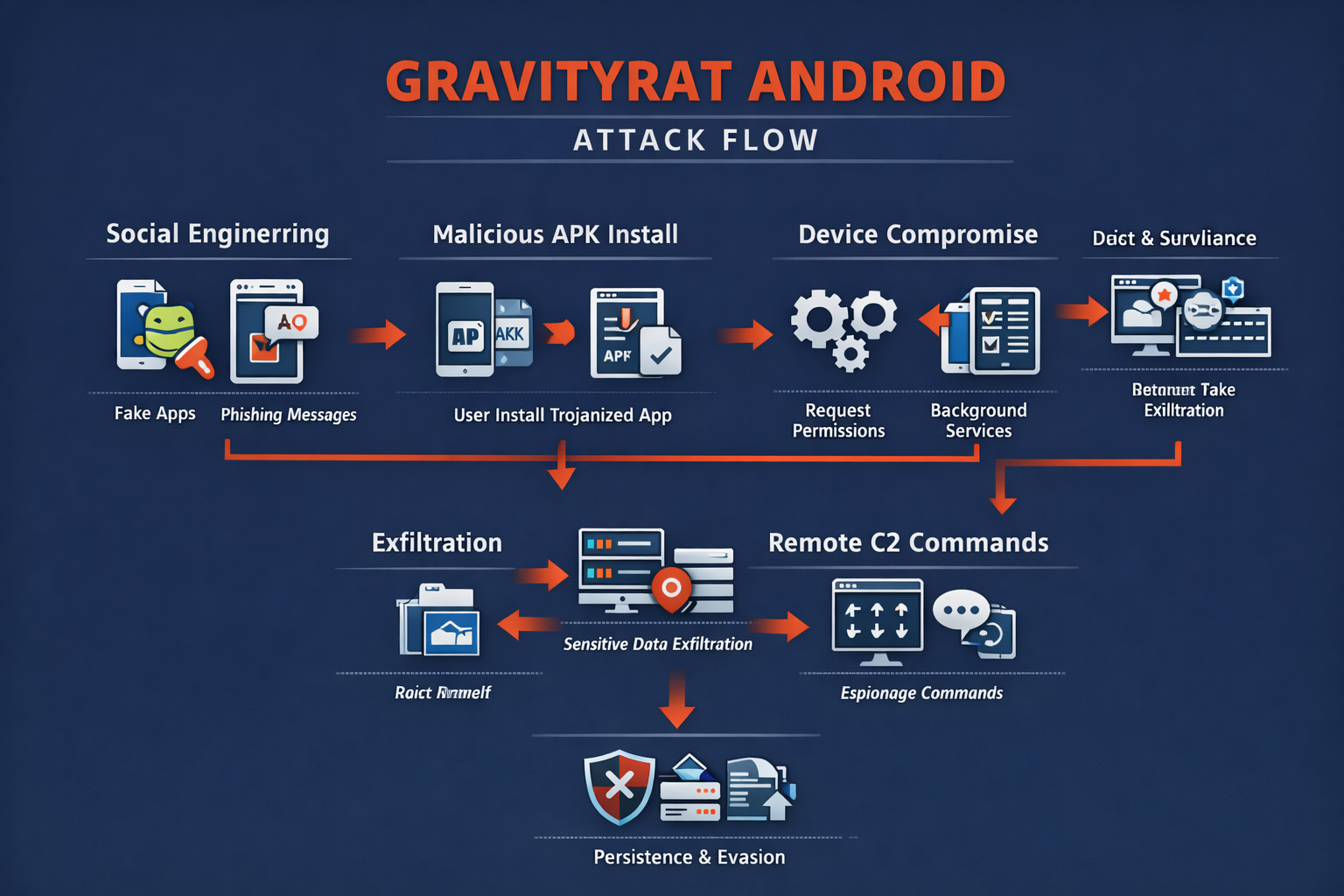
GravityRAT Is A Highly Sophisticated Android Malware Strain Categorized As A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) That Is Primarily Used For Cyber-espionage And Targeted Surveillance Operations. Originally Identified In Windows-based Espionage Campaigns, GravityRAT Later Evolved Into Mobile Platforms, Particularly Android, Reflecting The Growing Strategic Value Of Smartphones As Intelligence Collection Tools.
Unlike Financially Motivated Mobile Malware That Focuses On Banking Fraud Or Adware Revenue, GravityRAT Is Designed For Long-term Covert Monitoring, Data Exfiltration, And Persistent Device Control, Making It Especially Dangerous For Journalists, Government Officials, Military Personnel, Researchers, And Corporate Executives.
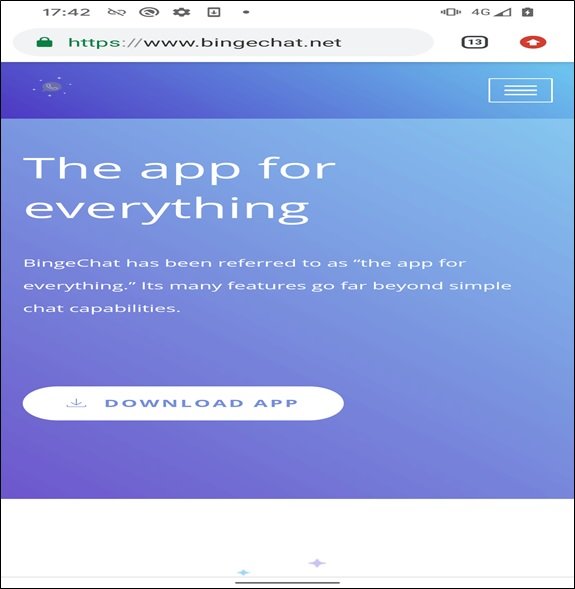
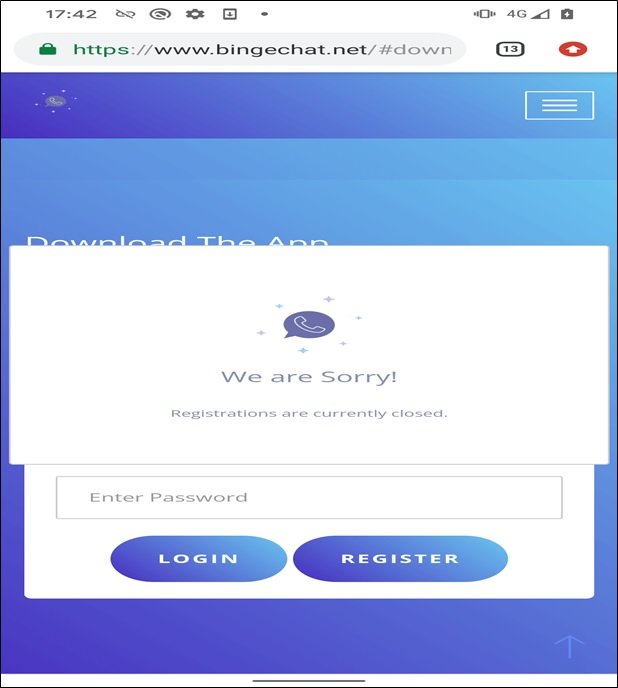
The Android Variant Of GravityRAT Is Typically Distributed Through Highly Targeted Social Engineering Campaigns, Often Masquerading As Legitimate Chat Applications, Secure Communication Tools, Cloud Storage Utilities, Or Productivity Apps. Victims Are Tricked Into Installing Trojanized APK Files Hosted On Third-party Websites Or Shared Through Messaging Platforms And Email Links.
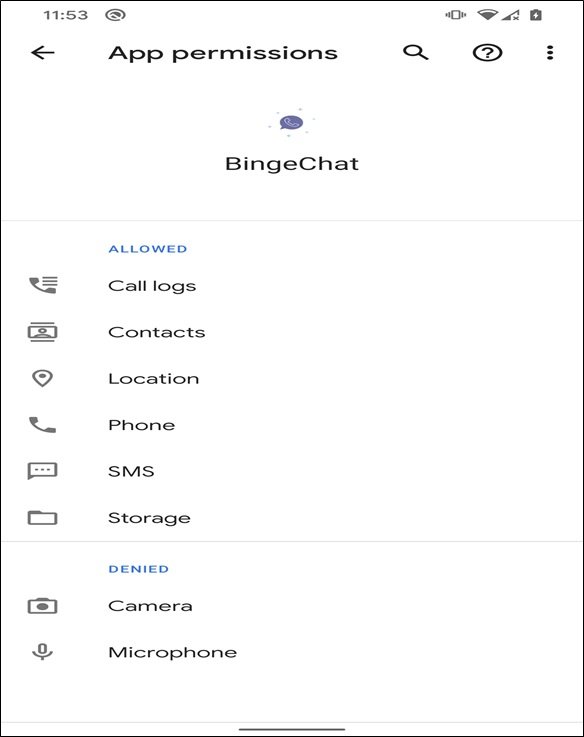
Once Installed, The Malware Silently Activates Background Services, Requests Extensive Permissions, And Establishes Encrypted Communication Channels With Remote Command-and-control (C2) Servers Operated By Threat Actors. Because Installation Usually Requires Enabling “Install From Unknown Sources,” The Malware Often Bypasses Google Play Protect’s Default Security Checks.
From An Architectural Standpoint, GravityRAT Android Malware Follows A Modular Design That Allows Attackers To Dynamically Deploy Or Activate Specific Surveillance Components Depending On Mission Requirements. This Flexibility Enables Threat Operators To Selectively Enable Microphone Recording, Camera Access, SMS Interception, Call Logs Collection, File System Harvesting, And GPS Tracking. The Modular Framework Also Supports Plugin-based Expansion, Allowing Attackers To Add New Capabilities Without Reinstalling The Application, Thereby Maintaining Long-term Operational Stealth.
After Installation, GravityRAT Performs An Extensive Reconnaissance Phase To Gather Device-specific Metadata. This Includes Android Version, Device Model, IMEI Number, IMSI Identifier, Installed Application List, Network Information, And Battery Status. This Profiling Data Helps Attackers Classify Victims And Prioritize High-value Targets. The Collected Metadata Is Transmitted To C2 Servers Using Encrypted Communication Protocols That Blend With Legitimate HTTPS Traffic, Making Detection By Network Security Tools Extremely Challenging.
One Of The Most Dangerous Capabilities Of GravityRAT Is Its Ability To Exfiltrate Sensitive Personal And Organizational Data Directly From Infected Devices. The Malware Can Harvest Contact Lists, SMS Messages, Call Histories, Photos, Videos, Documents, And Application Databases. In Espionage Scenarios, Attackers Specifically Target Messaging Apps, Email Clients, And Cloud Storage Folders Where Confidential Conversations And Documents May Reside. Stolen Data Is Compressed, Encrypted, And Transmitted To Remote Servers In Small Chunks To Avoid Triggering Abnormal Data Transfer Alerts.
GravityRAT Also Functions As A Full-featured Remote Surveillance Tool. Operators Can Remotely Activate The Device Microphone To Record Ambient Conversations, Enabling Physical Surveillance Without Physical Proximity. The Malware Can Also Silently Capture Images Using The Front Or Rear Camera, Potentially Gathering Visual Intelligence From Meetings Or Secure Locations. GPS Tracking Features Allow Continuous Monitoring Of Victim Movement Patterns, Revealing Daily Routines, Travel Routes, And Frequently Visited Locations, Which Is Particularly Useful In Intelligence-gathering Operations.
Persistence Is Another Defining Characteristic Of GravityRAT Android Malware. The Application Disguises Itself As A Legitimate System Or Communication Service And Hides Its Icon After Installation, Making Manual Detection Difficult For Users. It Registers Background Services That Restart Automatically After Device Reboots And Monitors System Events To Maintain Operational Continuity. Some Variants Also Attempt To Prevent Uninstallation By Disabling Administrator Removal Options Or Reactivating Themselves Through Secondary Components If The Primary Service Is Terminated.
To Evade Security Detection, GravityRAT Incorporates Multiple Anti-analysis Techniques. These Include Code Obfuscation, Encrypted Configuration Files, Dynamic Payload Loading, And Delayed Execution Logic To Bypass Sandbox Environments. The Malware May Also Detect Emulator Environments Commonly Used By Malware Researchers And Alter Its Behavior To Avoid Revealing Its Full Capabilities. Frequent Updates And Variant Generation Further Reduce The Effectiveness Of Signature-based Mobile Antivirus Solutions.
The Command-and-control Infrastructure Used By GravityRAT Campaigns Is Often Geographically Distributed And Dynamically Updated. Attackers Rotate Server Domains And IP Addresses To Avoid Takedown Operations. Some Campaigns Use Compromised Legitimate Websites As Relay Nodes, Making Traffic Appear Benign And Trustworthy. This Infrastructure Resilience Ensures Long-term Access To Infected Devices Even When Individual Servers Are Blocked By Security Providers.
GravityRAT Is Strongly Associated With Targeted Espionage Campaigns Rather Than Mass Infection Operations. Unlike Typical Android Malware That Spreads Through Large-scale Ad Networks Or Fake Apps On Unofficial Stores, GravityRAT Relies On Spear-phishing Techniques And Personalized Social Engineering. Victims Often Receive Messages Referencing Professional Activities, Conferences, Job Opportunities, Or Secure Document Exchanges, Increasing Trust And Installation Likelihood. This Targeted Approach Significantly Increases Infection Success Rates While Minimizing Detection Exposure.
The Strategic Objectives Behind GravityRAT Deployments Often Involve Political Intelligence Gathering, Diplomatic Surveillance, And Corporate Espionage. Compromised Smartphones Provide Access Not Only To Digital Communications But Also To Real-world Behavioral Intelligence. This Dual Digital-physical Surveillance Capability Makes Mobile RATs Extremely Valuable To State-sponsored Threat Groups And Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Operations Seeking Long-term Monitoring Of Specific Individuals Or Organizations.
Detecting GravityRAT Infections On Android Devices Is Challenging Due To Stealth Techniques And Legitimate-looking App Behavior. Common Indicators Include Unusual Battery Drain, Unexpected Data Usage, Unexplained Background Activity, Overheating, And Missing Application Icons. However, These Symptoms Are Not Definitive And May Be Mistaken For Normal Device Issues. Advanced Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) Solutions With Behavioral Monitoring Capabilities Are More Effective In Identifying Suspicious App Behaviors Related To Unauthorized Surveillance Activities.
Manual Removal Of GravityRAT Is Risky And Often Ineffective, Especially When Persistence Mechanisms Are Deeply Embedded. Uninstalling The Visible App May Not Remove Background Services Or Secondary Components. In Confirmed Infection Cases, Security Experts Often Recommend Full Factory Resets Combined With Firmware Reinstallation To Eliminate Hidden Payloads. After Remediation, Users Must Immediately Change All Account Passwords, Revoke Active Sessions, And Monitor For Unauthorized Account Activity Across All Linked Services.
Prevention Remains The Most Effective Defense Against GravityRAT And Similar Android Espionage Malware. Users Should Avoid Installing APK Files From Unknown Or Unofficial Sources And Should Treat Unsolicited Links And Application Recommendations With Extreme Caution. Enterprises Should Enforce Mobile Device Management (MDM) Policies That Restrict Sideloading, Enforce OS Updates, And Monitor Application Behavior. Strong Application Permission Management And Regular Security Patching Significantly Reduce Attack Surface.
For Organizations, Mobile Security Should Be Integrated Into Broader Cybersecurity Strategies. Smartphones Often Have Access To Corporate Email, VPN Connections, Cloud Storage, And Collaboration Tools, Making Them Critical Endpoints In Enterprise Networks. Compromised Mobile Devices Can Serve As Entry Points For Broader Organizational Breaches, Enabling Attackers To Harvest Credentials And Pivot Into Internal Systems. Therefore, Endpoint Security Must Extend Beyond Desktops And Servers To Include Mobile Platforms.
The Evolution Of GravityRAT Highlights A Broader Trend In Cyber Warfare Where Smartphones Are Increasingly Targeted For Intelligence Operations. As Mobile Devices Become Central To Professional And Personal Life, They Accumulate Sensitive Data That Previously Resided On Secured Office Systems. This Shift Creates New Vulnerabilities That Traditional Perimeter-based Security Models Cannot Address Effectively. Advanced Mobile Malware Like GravityRAT Exploits This Gap By Operating Entirely Within Personal Devices While Accessing Organizational Information.
From A Cybersecurity Research Perspective, GravityRAT Represents An Important Case Study In Cross-platform Malware Evolution. Its Transition From Windows-based Surveillance To Mobile Platforms Demonstrates How Threat Actors Adapt Tools To Changing User Behavior Patterns. Studying Such Malware Provides Insights Into Attacker Tradecraft, Operational Security Measures, And Long-term Campaign Management Strategies, Which Are Essential For Developing More Resilient Mobile Defense Mechanisms.
Legal And Regulatory Implications Of Mobile Espionage Are Also Growing Concerns. Data Exfiltration From Compromised Devices May Involve Violations Of Privacy Laws, Corporate Compliance Requirements, And National Security Regulations. Organizations Impacted By Such Breaches May Face Regulatory Penalties, Reputational Damage, And Legal Liability If Sensitive Customer Or Employee Data Is Compromised Through Infected Mobile Endpoints. Therefore, Proactive Mobile Security Investments Are Not Only Technical Necessities But Also Compliance Imperatives.
In Conclusion, GravityRAT Android Malware Is A Highly Advanced And Stealthy Surveillance Threat Designed For Targeted Espionage Operations Rather Than Opportunistic Cybercrime. Its Modular Architecture, Persistent Control Mechanisms, Extensive Data Harvesting Capabilities, And Sophisticated Evasion Techniques Make It Particularly Dangerous And Difficult To Detect.
With Smartphones Now Serving As Critical Communication And Data Storage Hubs, Infections Can Lead To Severe Privacy Violations, Corporate Espionage, And National Security Risks. Defending Against Such Threats Requires Strict Mobile Security Practices, Continuous Monitoring, User Awareness Training, And Integration Of Mobile Endpoints Into Enterprise Cybersecurity Frameworks. As Mobile Espionage Campaigns Continue To Evolve, Threats Like GravityRAT Will Remain At The Forefront Of Modern Cyber Intelligence Operations.
Step 1: Boot Into Safe Mode
Restart Your PC And Press F8 (or Shift + F8 For Some Systems) Before Windows Loads.
Choose Safe Mode With Networking.
Safe Mode Prevents Most Malware From Loading.
Press Win + R, Type appwiz.cpl, And Press Enter.
Sort By Install Date And Uninstall Unknown Or Recently Added Programs.
Use A Trusted Anti-malware Tool:
Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com
Screenshot Of Malwarebytes - Visit Links
Microsoft Defender – Built Into Windows 10/11
HitmanPro, ESET Online Scanner, Or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
VIPRE Antivirus - US And Others Countries, | India
Run A Full Scan And Delete/quarantine Detected Threats.
Win + R, Type temp → Delete All Files.Press Win + R, Type %temp% → Delete All Files.
Use Disk Cleanup: cleanmgr In The Run Dialog.
Go To: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Open hosts File With Notepad.
Replace With Default Content:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Open Task Manager
Go To Startup Tab
Disable Any Suspicious Entries.
Open Command Prompt As Administrator.
Run These Commands:
netsh Winsock Reset
netsh Int Ip Reset
ipconfig /flushdns
Unwanted Homepage Or Search Engine
Pop-ups Or Redirects
Unknown Extensions Installed
For Chrome:
Go To: chrome://extensions/
Remove Anything Unfamiliar
For Firefox:
Go To: about:addons → Extensions
Remove Suspicious Add-ons
For Edge:
Go To: edge://extensions/
Uninstall Unknown Add-ons
Chrome:
Go To chrome://settings/reset → "Restore Settings To Their Original Defaults"
Firefox:
Go To about:support → "Refresh Firefox"
Edge:
Go To edge://settings/resetProfileSettings → "Reset Settings"
All Browsers:
Use Ctrl + Shift + Del → Select All Time
Clear Cookies, Cached Files, And Site Data
Make Sure They Are Not Hijacked.
Chrome: chrome://settings/search
Firefox: about:preferences#search
Edge: edge://settings/search
Chrome: chrome://settings/cleanup
Use Malwarebytes Browser Guard For Real-time Browser Protection.
Always Download Software From Trusted Sources.
Keep Windows, Browsers, And Antivirus Updated.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links Or Ads.
Use ad Blockers And reputable Antivirus Software.
Backup Your Files Regularly.
To Remove Malware From Your Windows PC, Start By Booting Into Safe Mode, Uninstalling Suspicious Programs, And Scanning With Trusted Anti-malware Tools Like Malwarebytes. Clear Temporary Files, Reset Your Network Settings, And Check Startup Apps For Anything Unusual.
For web Browsers, Remove Unwanted Extensions, Reset Browser Settings, Clear Cache And Cookies, And Ensure Your Homepage And Search Engine Haven’t Been Hijacked. Use Cleanup Tools Like Chrome Cleanup Or Browser Guard For Added Protection.
?? Prevention Tips: Keep Software Updated, Avoid Suspicious Downloads, And Use Antivirus Protection Plus Browser Ad Blockers. Regular Backups Are Essential.
Why It Matters: Not All VPNs Offer Malware Protection.
What To Look For: Providers With built-in Malware/ad/tracker Blockers (e.g., NordVPN’s Threat Protection, ProtonVPN’s NetShield).
Purpose: Prevents Data Leaks If Your VPN Connection Drops.
Benefit: Ensures Your Real IP And Browsing Activity Aren’t Exposed To Malware-distributing Websites.
Why It Matters: DNS Leaks Can Expose Your Online Activity To Attackers.
Solution: Enable DNS Leak Protection In Your VPN Settings Or Use A Secure DNS Like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Risk: Free VPNs Often Contain Malware, Sell User Data, Or Lack Security Features.
Better Option: Use Reputable Paid VPNs That Offer security Audits And Transparent Privacy Policies.
Some VPNs Block Known Phishing And Malicious Sites.
Example: Surfshark’s CleanWeb, CyberGhost’s Content Blocker.
Reason: Security Patches Fix Known Vulnerabilities.
Tip: Enable Auto-updates Or Check For Updates Weekly.
Scope: Malware Can Enter Through Phones, Tablets, Or IoT Devices.
Solution: Install VPN Apps On Every Internet-connected Device.
Fact: VPNs Do Not Remove Or Detect Malware On Your System.
Complement It With:
Antivirus Software
Firewall
Browser Extensions For Script Blocking
VPN Encrypts Traffic But Can’t Stop Malware From Executing If You Download Infected Files.
Split Tunneling Allows Certain Apps/sites To Bypass VPN.
Tip: Never Exclude Browsers, Email Clients, Or Download Managers From VPN Tunneling.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) Enhances Your Online Privacy By Encrypting Your Internet Traffic And Masking Your IP Address. It Protects Your Data On Public Wi-Fi, Hides Browsing Activity From Hackers And ISPs, And Helps Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs Also Add A Layer Of Defense Against Malware By Blocking Malicious Websites And Trackers When Using Advanced Features. However, A VPN Does Not Remove Existing Malware Or Act As Antivirus Software. For Full Protection, Combine VPN Use With Antivirus Tools, Regular Software Updates, And Cautious Browsing Habits. Always Choose A Reputable VPN Provider With Strong Security And Privacy Policies.
GravityRat Android Malware, Remove GravityRat Android Malware, Uninstall GravityRat Android Malware, GravityRat Android Malware Removal, Get Rid Of Gr