 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
Cryptocurrency Has Reshaped The Digital Finance Landscape, But It Has Also Opened New Doors For Cybercriminals. One Such Growing Menace Is cryptojacking—a Stealthy Cyberattack Where Hackers Hijack Your Computing Power To Mine Digital Currencies Without Your Consent. Unlike Traditional Malware That Steals Data Or Locks Files For Ransom, Cryptojacking Is Quiet, Persistent, And Often Goes Undetected For Months, Silently Draining System Resources And Reducing Performance.
In This Blog, We’ll Explore What Cryptojacking Is, How It Works, Why It's Dangerous, And How Individuals And Organizations Can Prevent And Detect It.
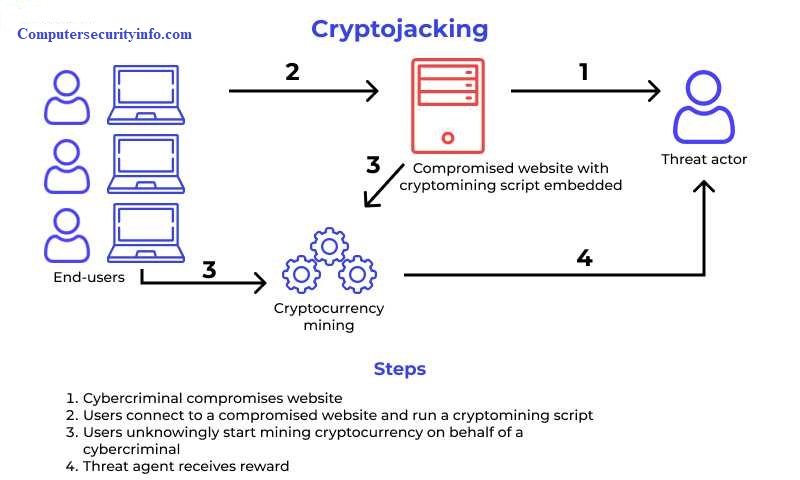
Cryptojacking (short For “cryptocurrency Hijacking”) Is A Type Of Cyberattack In Which A Hacker Uses Someone Else’s Computer, Smartphone, Server, Or Even Cloud Infrastructure To Mine Cryptocurrency. Instead Of Installing Mining Software On Their Own System, The Attacker Exploits Others’ Computing Power, Saving On Hardware Costs And Electricity Bills.
In Most Cases, Victims Are Unaware That Their Devices Have Been Compromised. The Result? Sluggish Performance, Overheating Systems, Higher Electricity Usage, And Even Hardware Failure In Extreme Cases—all While The Attacker Earns Cryptocurrency.
Cryptojacking Typically Takes Two Main Forms:
This Involves Infecting A Device With Cryptomining Malware. It Often Spreads Through:
Phishing Emails With Malicious Attachments Or Links
Trojanized Software That Installs Mining Code Secretly
Drive-by Downloads From Compromised Websites
Once Installed, The Malware Runs Silently In The Background, Using Your System’s CPU Or GPU To Mine Cryptocurrencies Like Monero, Which Is Preferred For Its Privacy-focused Design And Lower Resource Requirements.
Also Known As cryptomining Scripts, This Method Doesn’t Require Downloading Malware. Instead, Attackers Inject Mining Scripts Into Websites Or Online Ads. When A User Visits The Infected Page, The Script Runs In Their Browser And Starts Mining As Long As The Page Remains Open.
Initially, Some Legitimate Websites Used This Technique To Generate Revenue In Place Of Ads (using Services Like Coinhive, Now Defunct), But The Practice Was Widely Abused By Cybercriminals.
Cryptojacking Offers Several Advantages To Cybercriminals:
Stealth: It’s Designed To Stay Hidden And Often Doesn’t Alert The Victim.
Low Risk: There’s No Direct Theft Or Demand, So Victims Might Not Investigate.
Scalable: With Hundreds Or Thousands Of Infected Devices, Attackers Can Mine Substantial Cryptocurrency.
No Infrastructure Needed: Attackers Use Your Resources Instead Of Investing In Their Own Hardware.
Tesla Cloud Breach: In 2018, Attackers Gained Access To Tesla’s Kubernetes Console On AWS And Used It To Mine Cryptocurrency, Exploiting Unsecured Credentials.
YouTube Ads: Attackers Embedded Mining Scripts Into YouTube Ads, Using Viewers’ Systems For Mining While Watching Videos.
Government Websites: Several Government And University Websites Across The World Have Unknowingly Hosted Mining Scripts, Affecting Thousands Of Users.
Cryptojacking Is Stealthy, But There Are Signs To Watch For:
Slower Performance On Computers Or Mobile Devices
High CPU Or GPU Usage Even When Idle
Overheating Or Fan Running Constantly
Shorter Battery Life On Mobile Devices
Unexpected Crashes Or Freezes
Spike In Electricity Bills Or Cloud Service Usage
IT Professionals May Also Notice Unknown Processes Or Browser Tabs Consuming Disproportionate CPU Resources.
While PCs Are The Most Common Targets, Mobile Devices And IoT Gadgets (like Smart Cameras Or Routers) Are Increasingly Vulnerable. These Devices Often Have Weaker Security And Run Outdated Firmware, Making Them Easy Targets For Cryptojacking Malware.
On Mobile, Symptoms May Include Poor Battery Life, Overheating, And General Sluggishness. In IoT Devices, Cryptojacking May Not Be Noticeable Until The Hardware Fails Or Your Network Slows Down.
Preventing Cryptojacking Involves A Mix Of Tools, Awareness, And Best Practices:
Install Reputable Security Software And Keep It Updated. Many Modern Antivirus Programs Can Detect And Block Mining Scripts Or Cryptojacking Malware.
Use Extensions Like:
MinerBlock
No Coin
uBlock Origin (with Mining Filter Lists)
These Block Known Mining Scripts From Running In Your Browser.
Regularly Update Your Operating System, Browser, And Plugins. Vulnerabilities In Outdated Software Are Common Entry Points For Cryptojacking Scripts.
Most Cryptojacking Starts With A Click. Train Users To:
Avoid Suspicious Emails
Not Click On Untrusted Links
Download Software Only From Official Sources
Block Access To Known Mining Domains And URLs Using DNS Filtering Tools And Firewall Rules. This Can Prevent Devices From Communicating With Mining Pools.
Use System Monitoring Tools To Detect Unusual Spikes In CPU Usage Or Outbound Network Connections. Sudden Increases In Usage During Idle Times May Signal An Infection.
Although Disabling JavaScript May Break Some Web Functionality, It Can Help Block Browser-based Mining Scripts. Use This In High-risk Environments.
For Businesses And Enterprises, A Proactive Cybersecurity Strategy Is Essential:
Deploy Endpoint Detection And Response (EDR) Tools To Monitor Unusual Activity.
Implement Patch Management Policies To Ensure Software Stays Up To Date.
Segment Your Network To Isolate Infected Systems And Prevent Lateral Movement.
Create Incident Response Plans Specifically For Cryptojacking Detection And Removal.
Audit Resource Usage Regularly To Catch Anomalies.
Cloud Users Should Monitor Usage Dashboards (e.g., AWS, Azure) For Sudden Spikes That Could Indicate Cryptojacking Within Virtual Machines.
If You Suspect Cryptojacking, Take The Following Steps:
Disconnect From The Internet To Stop Ongoing Mining Activity.
Scan Your System Using A Trusted Antivirus Or Anti-malware Tool.
Check Running Processes For High CPU Consumption Or Unfamiliar Names.
Uninstall Suspicious Apps Or Browser Extensions.
Clear Your Browser Cache And Disable Extensions If The Issue Is Browser-based.
Restore From A Clean Backup If Malware Removal Is Not Successful.
Cryptojacking Is Likely To Grow As Cryptocurrencies Remain Profitable And As More Devices Connect To The Internet. Future Trends May Include:
AI-enhanced Malware That Adapts To Avoid Detection
Cryptojacking-as-a-service Offerings In The Cybercrime Underground
More Attacks On Cloud And Container Environments
Staying Ahead Means Constant Vigilance And Adaptation To Emerging Threats.
Cryptojacking May Be Silent, But Its Impact Is Loud—wasted Resources, Poor System Performance, And Rising Operational Costs. Unlike More Aggressive Attacks, It Often Flies Under The Radar, Making It Essential To Stay Educated And Protected.
Whether You're An Individual User, A Business Owner, Or A Security Professional, Understanding Cryptojacking Is The First Step In Combating It. Through Awareness, Strong Cybersecurity Practices, And The Right Tools, You Can Defend Your Systems From Becoming Unwitting Miners In A Criminal Operation.
Cryptojacking, What Is Cryptojacking, Cryptojacking Definition, Types Of Cryptojacking