 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
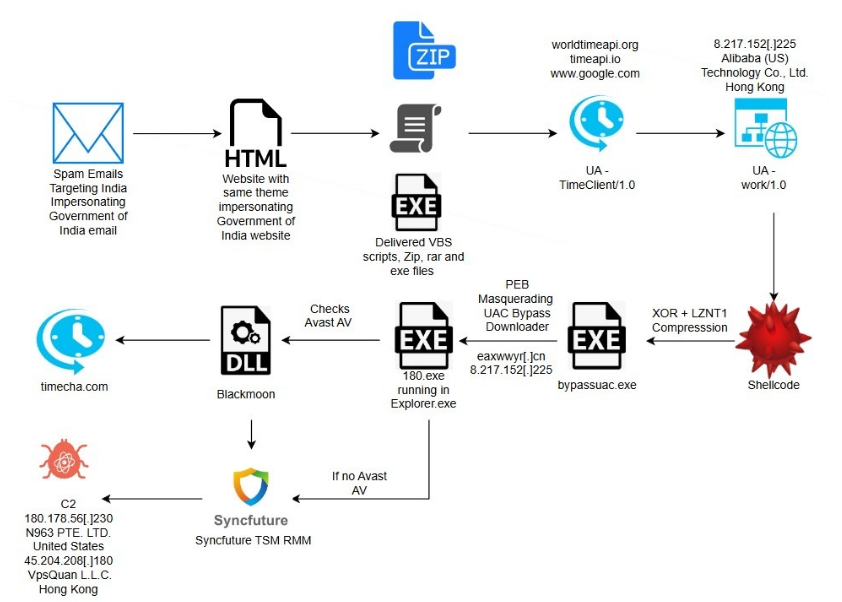
Malware Continues To Evolve At A Rapid Pace, Adapting To New Technologies, Operating Systems, And User Behaviors. Among The Many Threats That Have Surfaced Over The Years, Blackmoon Malware Stands Out As A Sophisticated And Stealthy Cyber Threat That Has Targeted Both Individual Users And Enterprise Environments. Known For Its Modular Design, Persistence Mechanisms, And Ability To Evade Traditional Security Tools, Blackmoon Malware Represents A Significant Challenge In Modern Cybersecurity.
This Article Provides An In-depth Analysis Of Blackmoon Malware, Covering Its Origins, Infection Vectors, Technical Behavior, Real-world Impact, Detection Methods, And Prevention Strategies. Whether You Are A Cybersecurity Professional, IT Administrator, Or Simply A Curious Reader, Understanding Blackmoon Malware Is Essential For Staying Protected In Today’s Threat Landscape.
Blackmoon Malware Is A Malicious Software Family Designed To Infiltrate Systems, Maintain Long-term Persistence, And Execute A Range Of Harmful Activities. It Is Often Categorized As A modular Malware Framework, Meaning It Can Download And Activate Additional Components Depending On The Attacker’s Objectives.
Unlike Simple Viruses Or Worms, Blackmoon Malware Is Typically Deployed As Part Of A targeted Campaign, Often Associated With Cybercrime Operations, Espionage Activities, Or Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). Its Flexibility Allows It To Function As:
A Data Stealer
A Backdoor For Remote Access
A Downloader For Secondary Payloads
A Reconnaissance Tool
This Adaptability Makes Blackmoon Malware Particularly Dangerous, As Its Behavior Can Change Over Time.
The Exact Origin Of Blackmoon Malware Remains Unclear, Which Is Common For Advanced Malware Families. Security Researchers Believe It First Appeared In Underground Forums And Private Cybercrime Toolkits Before Being Observed In The Wild.
Over Time, Blackmoon Malware Has Evolved Through Several Iterations:
Early Versions Focused On Basic System Compromise And Data Exfiltration.
Later Variants Introduced Encryption, Obfuscation, And Sandbox Evasion Techniques.
Modern Versions Leverage Fileless Execution, Memory Injection, And Command-and-control (C2) Encryption.
This Steady Evolution Suggests Ongoing Development By Skilled Threat Actors Who Actively Respond To Detection Efforts By Security Vendors.

Figure: Phishing Email Impersonating Income Tax Department Penalty Notice (Source: ESentire)
Understanding Infection Vectors Is Critical For Preventing Blackmoon Malware Attacks. Common Distribution Methods Include:
Phishing Remains The Most Effective Delivery Method For Blackmoon Malware. Attackers Send Emails Containing:
Malicious Attachments (PDFs, Word Documents, ZIP Files)
Links To Compromised Or Spoofed Websites
Social Engineering Messages Posing As Invoices, Job Offers, Or Security Alerts
Once The Victim Opens The Attachment Or Clicks The Link, The Malware Payload Is Silently Executed.
Blackmoon Malware May Be Delivered Through Compromised Websites Hosting Exploit Kits. Simply Visiting Such A Site With An Unpatched Browser Or Plugin Can Trigger A drive-by Download, Infecting The System Without User Interaction.
Unofficial Software Sources Are A Major Distribution Channel. Attackers Often Bundle Blackmoon Malware With:
Cracked Software
Fake Activation Tools
Modified Installers
Users Seeking Free Software Unknowingly Grant Full System Access To Attackers.
In Enterprise Environments, Blackmoon Malware Has Been Observed Exploiting Known Vulnerabilities In Operating Systems, VPN Appliances, Or Exposed Services To Gain Initial Access.
Blackmoon Malware Is Designed To Operate Quietly And Efficiently. Once Executed, It Follows A Multi-stage Process.
After Infection, Blackmoon Malware Attempts To Establish Persistence By:
Modifying Registry Keys
Creating Scheduled Tasks
Installing Malicious Services
Injecting Itself Into Legitimate System Processes
These Techniques Allow It To Survive System Reboots And Remain Active For Long Periods.
Blackmoon Malware Communicates With Remote Servers Controlled By Attackers. This Communication Is Typically:
Encrypted Using Custom Or Standard Algorithms
Hidden Within Legitimate Network Traffic
Routed Through Proxy Servers Or Compromised Hosts
Through C2 Channels, Attackers Can Issue Commands, Upload New Modules, Or Exfiltrate Stolen Data.
One Of Blackmoon Malware’s Most Dangerous Features Is Its Modular Design. Depending On Instructions From The C2 Server, It Can Load Modules That Enable:
Keylogging
Screenshot Capture
Credential Theft
File Exfiltration
Lateral Movement Within Networks
This Flexibility Allows Attackers To Tailor Their Activities To Specific Targets.
To Avoid Detection, Blackmoon Malware Employs Advanced Evasion Methods, Including:
Code Obfuscation And Packing
Anti-debugging Checks
Virtual Machine And Sandbox Detection
Fileless Execution Using PowerShell Or Memory Injection
These Techniques Make Analysis And Detection Significantly More Difficult.
The Impact Of Blackmoon Malware Varies Depending On The Target And Attacker Intent. However, Documented Cases Reveal Serious Consequences.
For Individual Users, Blackmoon Malware Can Lead To:
Stolen Login Credentials
Financial Fraud
Identity Theft
Loss Of Personal Data
In Many Cases, Victims Are Unaware Of The Infection Until Damage Has Already Occurred.
Organizations Face Even Greater Risks, Including:
Data Breaches Involving Sensitive Customer Information
Intellectual Property Theft
Disruption Of Business Operations
Regulatory Fines And Legal Consequences
Because Blackmoon Malware Can Act As A Backdoor, It Is Often Used As A Stepping Stone For Larger Attacks Such As Ransomware Deployment.
Persistent Infections Allow Attackers To Monitor Systems Over Time, Collecting Valuable Intelligence. This Long-term Access Is Particularly Dangerous For Government Agencies, Research Institutions, And Critical Infrastructure Providers.
Detecting Blackmoon Malware Can Be Challenging Due To Its Stealthy Nature, But It Is Not Impossible.
Rather Than Relying Solely On Signatures, Modern Security Tools Use Behavioral Analysis To Detect Suspicious Activity Such As:
Unusual Process Injection
Unexpected Network Connections
Unauthorized Credential Access
Behavior-based Detection Is One Of The Most Effective Defenses Against Blackmoon Malware.
EDR Solutions Provide Real-time Visibility Into Endpoint Activity And Can Identify Indicators Of Compromise Associated With Blackmoon Malware.
Monitoring Outbound Traffic For Unusual Patterns Or Encrypted Communications With Unknown Servers Can Help Identify C2 Activity.
Up-to-date Threat Intelligence Feeds Can Provide Indicators Such As Malicious IP Addresses, Domains, And File Hashes Linked To Blackmoon Malware Campaigns.
If Blackmoon Malware Infection Is Suspected, Immediate Action Is Required.
Isolate The Affected System From The Network To Prevent Lateral Movement.
Perform A Full System Scan Using Reputable Security Software.
Analyze Running Processes And Startup Items For Suspicious Entries.
Restore From A Clean Backup If Available.
Change All Compromised Credentials, Especially Those Used On The Infected System.
In Enterprise Environments, Incident Response Teams Should Conduct A Full Forensic Investigation To Determine The Scope Of The Compromise.
Prevention Remains The Most Effective Defense Against Blackmoon Malware.
Educating Users About Phishing, Suspicious Downloads, And Social Engineering Significantly Reduces Infection Rates.
Keeping Operating Systems, Applications, And Firmware Up To Date Closes Vulnerabilities Exploited By Attackers.
Deploying Next-generation Antivirus, EDR, And Firewall Solutions Provides Layered Protection Against Advanced Threats.
Limiting User Privileges Reduces The Damage Malware Can Cause If A System Is Compromised.
Maintaining Secure, Offline Backups Ensures Rapid Recovery In The Event Of A Serious Infection.
Blackmoon Malware Exemplifies The Trend Toward stealthy, Modular, And Persistent Threats. As Cybersecurity Defenses Improve, Attackers Respond With More Sophisticated Techniques Designed To Bypass Traditional Detection.
Future Variants Of Blackmoon Malware May Incorporate:
AI-assisted Evasion Techniques
More Advanced Fileless Execution Methods
Deeper Integration With Legitimate Cloud Services
This Ongoing Arms Race Highlights The Importance Of Proactive Security Strategies And Continuous Monitoring.
Sign Of Compromise:
For Detailed List Of IoC, Kindly Refer The Below URL:
Blackmoon Malware Is A Powerful And Adaptable Cyber Threat That Poses Serious Risks To Individuals And Organizations Alike. Its Modular Architecture, Stealthy Behavior, And Persistence Mechanisms Make It Particularly Challenging To Detect And Remove.
By Understanding How Blackmoon Malware Operates, How It Spreads, And How It Can Be Prevented, Users And Security Professionals Can Significantly Reduce Their Exposure To This Threat. In An Era Where Cyberattacks Are Increasingly Sophisticated, Knowledge Remains One Of The Strongest Defenses.
Staying Informed, Maintaining Strong Security Hygiene, And Investing In Modern Protection Tools Are Essential Steps Toward Safeguarding Systems Against Blackmoon Malware And Similar Advanced Threats.
Step 1: Boot Into Safe Mode
Restart Your PC And Press F8 (or Shift + F8 For Some Systems) Before Windows Loads.
Choose Safe Mode With Networking.
Safe Mode Prevents Most Malware From Loading.
Press Win + R, Type appwiz.cpl, And Press Enter.
Sort By Install Date And Uninstall Unknown Or Recently Added Programs.
Use A Trusted Anti-malware Tool:
Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com
Screenshot Of Malwarebytes - Visit Links
Microsoft Defender – Built Into Windows 10/11
HitmanPro, ESET Online Scanner, Or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
VIPRE Antivirus - US And Others Countries, | India
Run A Full Scan And Delete/quarantine Detected Threats.
Win + R, Type temp → Delete All Files.Press Win + R, Type %temp% → Delete All Files.
Use Disk Cleanup: cleanmgr In The Run Dialog.
Go To: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Open hosts File With Notepad.
Replace With Default Content:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Open Task Manager
Go To Startup Tab
Disable Any Suspicious Entries.
Open Command Prompt As Administrator.
Run These Commands:
netsh Winsock Reset
netsh Int Ip Reset
ipconfig /flushdns
Unwanted Homepage Or Search Engine
Pop-ups Or Redirects
Unknown Extensions Installed
For Chrome:
Go To: chrome://extensions/
Remove Anything Unfamiliar
For Firefox:
Go To: about:addons → Extensions
Remove Suspicious Add-ons
For Edge:
Go To: edge://extensions/
Uninstall Unknown Add-ons
Chrome:
Go To chrome://settings/reset → "Restore Settings To Their Original Defaults"
Firefox:
Go To about:support → "Refresh Firefox"
Edge:
Go To edge://settings/resetProfileSettings → "Reset Settings"
All Browsers:
Use Ctrl + Shift + Del → Select All Time
Clear Cookies, Cached Files, And Site Data
Make Sure They Are Not Hijacked.
Chrome: chrome://settings/search
Firefox: about:preferences#search
Edge: edge://settings/search
Chrome: chrome://settings/cleanup
Use Malwarebytes Browser Guard For Real-time Browser Protection.
Always Download Software From Trusted Sources.
Keep Windows, Browsers, And Antivirus Updated.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links Or Ads.
Use ad Blockers And reputable Antivirus Software.
Backup Your Files Regularly.
To Remove Malware From Your Windows PC, Start By Booting Into Safe Mode, Uninstalling Suspicious Programs, And Scanning With Trusted Anti-malware Tools Like Malwarebytes. Clear Temporary Files, Reset Your Network Settings, And Check Startup Apps For Anything Unusual.
For web Browsers, Remove Unwanted Extensions, Reset Browser Settings, Clear Cache And Cookies, And Ensure Your Homepage And Search Engine Haven’t Been Hijacked. Use Cleanup Tools Like Chrome Cleanup Or Browser Guard For Added Protection.
?? Prevention Tips: Keep Software Updated, Avoid Suspicious Downloads, And Use Antivirus Protection Plus Browser Ad Blockers. Regular Backups Are Essential.
Why It Matters: Not All VPNs Offer Malware Protection.
What To Look For: Providers With built-in Malware/ad/tracker Blockers (e.g., NordVPN’s Threat Protection, ProtonVPN’s NetShield).
Purpose: Prevents Data Leaks If Your VPN Connection Drops.
Benefit: Ensures Your Real IP And Browsing Activity Aren’t Exposed To Malware-distributing Websites.
Why It Matters: DNS Leaks Can Expose Your Online Activity To Attackers.
Solution: Enable DNS Leak Protection In Your VPN Settings Or Use A Secure DNS Like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Risk: Free VPNs Often Contain Malware, Sell User Data, Or Lack Security Features.
Better Option: Use Reputable Paid VPNs That Offer security Audits And Transparent Privacy Policies.
Some VPNs Block Known Phishing And Malicious Sites.
Example: Surfshark’s CleanWeb, CyberGhost’s Content Blocker.
Reason: Security Patches Fix Known Vulnerabilities.
Tip: Enable Auto-updates Or Check For Updates Weekly.
Scope: Malware Can Enter Through Phones, Tablets, Or IoT Devices.
Solution: Install VPN Apps On Every Internet-connected Device.
Fact: VPNs Do Not Remove Or Detect Malware On Your System.
Complement It With:
Antivirus Software
Firewall
Browser Extensions For Script Blocking
VPN Encrypts Traffic But Can’t Stop Malware From Executing If You Download Infected Files.
Split Tunneling Allows Certain Apps/sites To Bypass VPN.
Tip: Never Exclude Browsers, Email Clients, Or Download Managers From VPN Tunneling.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) Enhances Your Online Privacy By Encrypting Your Internet Traffic And Masking Your IP Address. It Protects Your Data On Public Wi-Fi, Hides Browsing Activity From Hackers And ISPs, And Helps Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs Also Add A Layer Of Defense Against Malware By Blocking Malicious Websites And Trackers When Using Advanced Features. However, A VPN Does Not Remove Existing Malware Or Act As Antivirus Software. For Full Protection, Combine VPN Use With Antivirus Tools, Regular Software Updates, And Cautious Browsing Habits. Always Choose A Reputable VPN Provider With Strong Security And Privacy Policies.
Blackmoon Malware, Blackmoon Virus, Malware Threat Analysis, Cyber Security Threats, Malware Detection And Prevention, Advanced Malware Attacks