 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
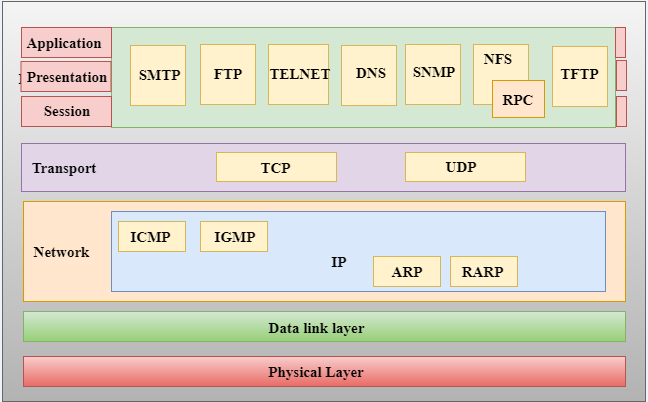
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Is A Set Of Communication Protocols Used For Transmitting Data Over The Internet And Other Computer Networks. It Is The Foundation Of The Internet And The Most Widely Used Network Protocol In The World.
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite Consists Of Several Protocols That Work Together To Enable Communication Between Devices. The Main Protocols Include:
IP (Internet Protocol): This Protocol Is Responsible For Routing Data Packets Between Devices And Ensuring That The Data Is Transmitted Accurately.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): This Protocol Provides Reliable, Ordered Delivery Of Data Between Applications Running On Different Devices. It Breaks Data Into Smaller Packets And Reassembles Them At The Receiving End.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): This Protocol Is Used For Transmitting Data That Does Not Require Reliable Delivery, Such As Video And Audio Streaming.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): This Protocol Is Used For Transmitting Web Pages And Other Data Over The Internet.
DNS (Domain Name System): This Protocol Is Used For Converting Domain Names Into IP Addresses, Allowing Users To Access Websites Using Human-readable Names Instead Of IP Addresses.
These Protocols Work Together To Enable The Transmission Of Data Over The Internet And Other Networks. The TCP/IP Protocol Suite Is Widely Used And Widely Supported, Making It The Preferred Choice For Communication On The Internet And Other Networks.
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite Consists Of Several Layers, Each With Its Own Specific Functions:
Application Layer: This Layer Provides Services To The User, Such As Email, File Transfer, And Web Browsing. It Is Responsible For Ensuring That The Data Being Transmitted Is In The Correct Format For The Application.
Transport Layer: This Layer Is Responsible For Ensuring Reliable Communication Between Applications Running On Different Devices. The Main Protocols At This Layer Are TCP And UDP, As Mentioned In The Previous Answer.
Network Layer: This Layer Is Responsible For Routing Data Between Devices. The Main Protocol At This Layer Is IP, Which Provides Routing And Addressing Functions.
Data Link Layer: This Layer Provides Physical Transmission Of Data Between Devices And Is Responsible For The Error-free Transmission Of Data. It Includes Protocols For Accessing The Physical Media And For Transmitting Data Frames Between Devices.
Physical Layer: This Layer Defines The Physical Characteristics Of The Network, Such As The Type Of Cabling And Signaling Used. It Is Responsible For Transmitting Raw Bits Of Data Over The Physical Media.
Each Layer Is Responsible For Performing Specific Functions, And Data Is Passed From One Layer To The Next As It Is Transmitted Between Devices. This Layered Approach Allows For Modularity And Scalability, Making It Possible To Add New Functionality Or Improve Existing Functionality Without Affecting The Other Layers.
The Network Access Layer Is Also Known As The Data Link Layer, Which Is The Second Layer In The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model. This Layer Provides Physical Transmission Of Data Between Devices And Is Responsible For The Error-free Transmission Of Data. It Includes Protocols For Accessing The Physical Media And For Transmitting Data Frames Between Devices.
The Main Functions Of The Network Access Layer Include:
Framing: Breaking Down Data Into Manageable Frames For Transmission.
Addressing: Assigning Unique Addresses To Each Device On The Network.
Flow Control: Regulating The Flow Of Data Between Devices To Prevent Data Overload.
Error Detection And Correction: Detecting And Correcting Any Errors That Occur During Transmission.
Media Access Control: Managing Access To The Physical Media And Ensuring That Only One Device Can Transmit Data At A Time.
The Network Access Layer Is Responsible For Transmitting Data Over The Physical Media, Such As Ethernet Cables, And Providing The Necessary Functionality To Ensure That Data Is Transmitted Reliably And Securely. The Network Access Layer Is An Important Part Of The Overall Communication Process In Computer Networks And Plays A Crucial Role In Ensuring The Smooth And Reliable Transmission Of Data.
The Internet Layer In The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Protocol Suite Is Responsible For Routing Data Between Devices On A Network. The Main Protocol At This Layer Is IP (Internet Protocol), Which Provides Routing And Addressing Functions.
The Main Functions Of The Internet Layer Include:
Addressing: IP Assigns Unique IP Addresses To Each Device On The Network, Allowing Data To Be Routed To The Correct Device.
Routing: IP Is Responsible For Routing Data Between Devices, Determining The Best Path For Data To Travel Based On Network Conditions And Availability.
Packet Fragmentation And Reassembly: IP Breaks Large Data Packets Into Smaller Fragments For Transmission And Reassembles Them At The Receiving End.
Error Detection: IP Can Detect Errors In Data Transmission And Request That The Data Be Retransmitted If Necessary.
The Internet Layer Is Responsible For Providing The Underlying Infrastructure For Transmitting Data Over The Internet And Other Networks. It Ensures That Data Is Transmitted Accurately And Efficiently, And That It Is Routed To The Correct Destination. The Internet Layer Is An Important Part Of The Overall Communication Process In Computer Networks And Plays A Crucial Role In Ensuring The Reliable And Secure Transmission Of Data.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Is A Protocol Used In The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Protocol Suite To Map An IP Address To A Physical (MAC) Address On A Network.
Each Device On A Network Has Both An IP Address And A MAC Address. The IP Address Is Used To Route Data Between Devices, While The MAC Address Is Used To Physically Deliver Data To A Specific Device On The Network.
When A Device Wants To Send Data To Another Device On The Same Network, It Needs To Determine The MAC Address Of The Destination Device. The ARP Protocol Is Used For This Purpose. The Sending Device Broadcasts An ARP Request On The Network, Asking For The MAC Address Of The Device With A Specific IP Address. The Device With That IP Address Responds With Its MAC Address, And The Sending Device Can Then Use That Information To Send The Data Directly To The Destination Device.
In This Way, ARP Is Responsible For Mapping IP Addresses To MAC Addresses On A Network, And Is An Essential Part Of The Communication Process In Computer Networks. It Helps Ensure That Data Is Delivered Accurately And Efficiently, And Is A Key Component Of The Overall Functioning Of The TCP/IP Protocol Suite.
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Is A Network Protocol Used In The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Protocol Suite For Error Reporting And Status Information. It Operates At The Network Layer Of The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model.
ICMP Is Used For A Variety Of Purposes, Including:
Echo Request/Reply (ping): Used To Test The Reachability Of A Network Device And Measure The Round-trip Time For Packets To Travel From The Source To The Destination And Back.
Destination Unreachable: Sent By Routers To Indicate That A Destination Network Or Host Is Unreachable.
Time Exceeded: Sent By Routers To Indicate That A Packet Was Discarded Because It Exceeded The Maximum Time Allowed For It To Traverse The Network.
Redirect: Sent By Routers To Inform A Host That It Should Send Its Packets To A Different Next-hop IP Address.
Router Discovery/Advertisement: Used By Routers To Discover Each Other And Exchange Information About Their Networks.
ICMP Is An Important Part Of The Overall Communication Process In Computer Networks, Providing Feedback And Status Information To Help Diagnose And Resolve Network Problems. It Helps Ensure That Data Is Transmitted Accurately And Efficiently, And Is A Key Component Of The Overall Functioning Of The TCP/IP Protocol Suite.
The Transport Layer In The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Protocol Suite Is Responsible For The Reliable Transmission Of Data Between Applications On Different Devices. The Main Protocols At This Layer Are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) And UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
The Main Functions Of The Transport Layer Include:
End-to-end Communication: The Transport Layer Provides A Communication Channel Between Applications On Different Devices, Allowing Them To Send And Receive Data.
Segmentation And Reassembly: The Transport Layer Breaks Large Data Into Smaller Segments For Transmission And Reassembles Them At The Receiving End.
Reliability: TCP Provides Reliable, Error-free Data Transmission By Using Flow Control, Error Checking, And Retransmission Of Lost Or Corrupted Packets.
Congestion Control: TCP Adjusts The Rate At Which Data Is Transmitted To Prevent Network Congestion And Maintain Network Efficiency.
Multiplexing: The Transport Layer Allows Multiple Applications To Share A Single Network Connection By Using Port Numbers To Differentiate Between Different Applications.
The Transport Layer Is Responsible For Ensuring That Data Is Transmitted Accurately And Reliably Between Applications On Different Devices. It Provides The Underlying Infrastructure For Transmitting Data, And Is An Essential Part Of The Overall Communication Process In Computer Networks. The Transport Layer Is A Key Component Of The Overall Functioning Of The TCP/IP Protocol Suite, And Plays A Crucial Role In Ensuring The Reliable And Secure Transmission Of Data Over Networks.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Is A Standard Network Protocol Used For The Transfer Of Files Between A Client And A Server Over A TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Network. FTP Operates At The Application Layer Of The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model.
The Main Features Of FTP Include:
File Transfer: FTP Enables The Transfer Of Files Between A Client And A Server, Allowing Users To Upload And Download Files.
User Authentication: FTP Requires A User To Provide A Username And Password For Authentication Before Accessing The Server.
Directory Listing: FTP Allows Users To List The Contents Of A Directory On The Server, Including Files And Subdirectories.
File Transfer Modes: FTP Supports Two File Transfer Modes: ASCII Mode For Text Files, And Binary Mode For Binary Files Such As Images, Audio, And Video.
Error Checking: FTP Uses Error Checking To Ensure That Files Are Transferred Accurately And Completely, And Provides Mechanisms For Resuming A Transfer In The Case Of A Connection Failure.
FTP Is Widely Used For The Transfer Of Files Over The Internet, Especially For Large Files That Cannot Be Sent As Email Attachments. It Is A Simple And Efficient Way To Transfer Files Between A Client And A Server, And Is Widely Supported By A Variety Of Operating Systems And Applications. FTP Is An Essential Tool For Many Businesses And Individuals, And Plays A Crucial Role In The Transfer Of Data Over Networks.
The Application Layer In The TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) Protocol Suite Provides The Interface Between The User Applications And The Underlying Network Infrastructure. It Operates At The Topmost Layer Of The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Model.
The Main Functions Of The Application Layer Include:
Application Services: The Application Layer Provides A Range Of Services To The User Applications, Including File Transfer (FTP), Email (SMTP), Web Browsing (HTTP), And Remote Login (Telnet).
User Interface: The Application Layer Provides A User-friendly Interface For Accessing Network Services, Allowing Users To Interact With The Network Through A Graphical User Interface (GUI) Or A Command-line Interface (CLI).
Data Representation: The Application Layer Is Responsible For Encoding And Decoding The Data Used By The Applications, Ensuring That Data Is Transmitted In A Standardized Format.
Interoperability: The Application Layer Provides A Standardized Interface For Different Applications To Interact With Each Other And With The Network, Ensuring Interoperability Between Different Systems.
The Application Layer Is The Highest Layer In The TCP/IP Protocol Suite And Is Responsible For Providing The Network Services That Users Interact With Directly. It Is The Interface Between The User Applications And The Underlying Network Infrastructure, And Plays A Crucial Role In The Overall Functioning Of The TCP/IP Protocol Suite. The Application Layer Is An Essential Component Of Computer Networks, Providing The Services That Enable Users To Access And Interact With The Network.
TCP/IP Protocol, Describe TCP/IP Protocol, Definit