 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
DNS Security Refers To The Measures And Techniques Used To Protect The Domain Name System (DNS) From Attacks And Vulnerabilities. The DNS Is A Critical Component Of The Internet Infrastructure, And Any Compromise To Its Security Can Have Far-reaching Consequences.
There Are Several Types Of DNS Attacks That Can Be Carried Out, Including:
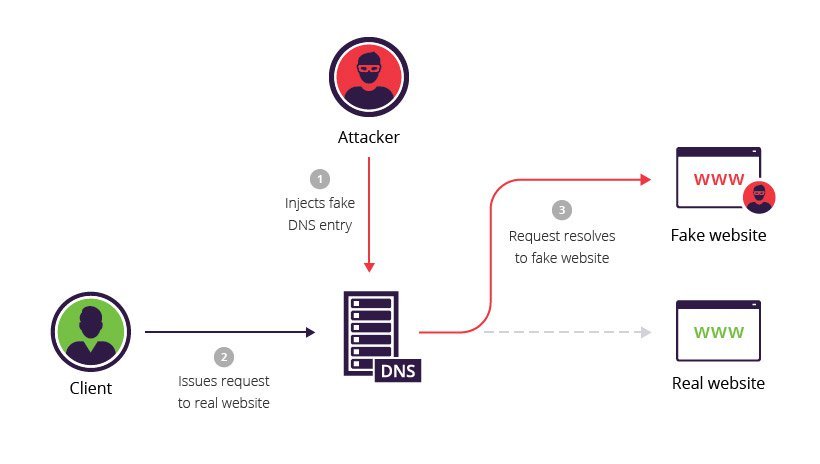
DNS Spoofing Or Cache Poisoning: This Is When An Attacker Injects False DNS Data Into A DNS Resolver's Cache, Causing It To Return Incorrect Results When A User Requests A DNS Lookup.
DNS Amplification: This Is When An Attacker Sends A DNS Query To A Vulnerable DNS Server, Which Then Responds With A Much Larger Answer Than The Original Query, Causing A Distributed Denial Of Service (DDoS) Attack.
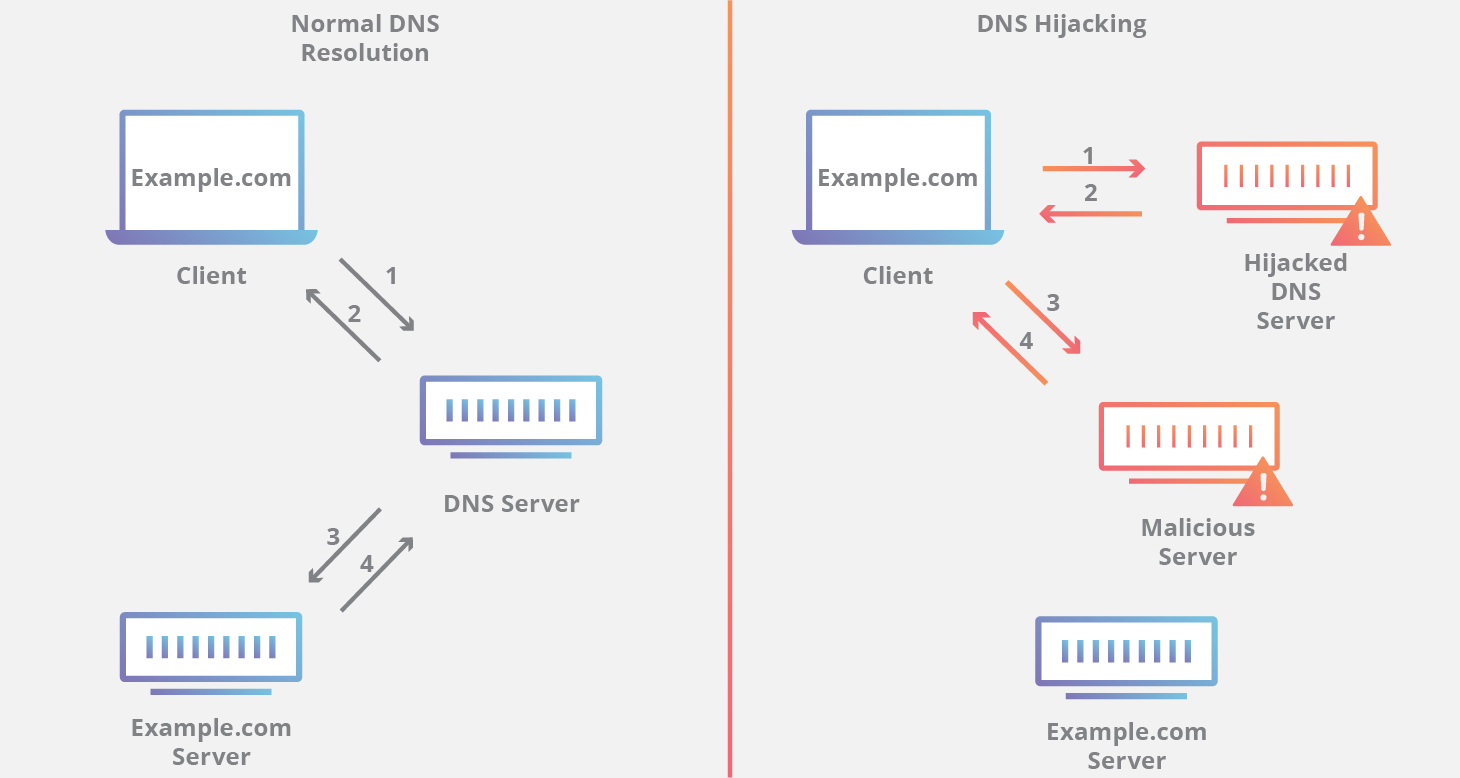
DNS Hijacking: This Is When An Attacker Gains Control Of A Domain Name Or Its Authoritative DNS Server, Allowing Them To Redirect Traffic To Their Own Malicious Site.
To Protect Against These Types Of Attacks, Several DNS Security Measures Have Been Developed, Including:
DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions): This Is A Set Of DNS Protocol Extensions That Provide Data Origin Authentication And Data Integrity Verification For DNS Information. It Helps To Prevent DNS Spoofing Attacks And Ensures That The DNS Data Being Returned To The User Is Legitimate.
DNS Filtering: This Is The Process Of Using DNS To Block Access To Malicious Websites, Such As Those Associated With Phishing, Malware, Or Botnets. DNS Filtering Can Be Done Using Various Techniques Such As Blacklisting, Whitelisting, And Content Filtering.
Two-factor Authentication: This Is The Process Of Requiring Two Different Methods Of Authentication Before Granting Access To A DNS Service. This Can Include A Password And A One-time Code Sent To The User's Mobile Phone.
Overall, DNS Security Is An Essential Aspect Of The Internet Infrastructure And Requires Ongoing Vigilance And Protection To Ensure Its Integrity And Reliability.
Yes, DNS Can Affect The Email Function In Several Ways. DNS Is An Essential Component Of The Email System, As It Is Used To Resolve The Domain Names And IP Addresses Of Email Servers, And To Ensure That Email Messages Are Delivered To The Correct Recipient.
Here Are A Few Ways In Which DNS Can Impact Email Function:
DNS Resolution Errors: If There Are Errors In The DNS Configuration, Such As Incorrect Or Missing DNS Records, It Can Prevent Email Messages From Being Delivered. For Example, If The MX Record For The Recipient's Domain Is Missing Or Misconfigured, Email Messages May Be Bounced Back To The Sender.
DNS Blacklisting: Some Email Servers Use DNS-based Blacklists To Identify And Block Email From Known Sources Of Spam Or Other Malicious Activity. If Your Email Server's IP Address Is Listed On One Of These Blacklists, It Can Prevent Your Email Messages From Being Delivered To Certain Recipients.
SPF And DKIM: SPF (Sender Policy Framework) And DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Are DNS-based Email Authentication Mechanisms That Are Used To Prevent Email Spoofing And Ensure That Email Messages Are Delivered Securely. If Your DNS Records Are Not Properly Configured To Support SPF And DKIM, It Can Cause Email Delivery Issues.
DNS Caching: As We Mentioned Earlier, DNS Servers Cache Information About Domain Names And IP Addresses To Reduce The Time It Takes To Resolve DNS Queries. However, If DNS Caching Is Not Properly Managed, It Can Lead To Delays In Email Delivery, Or Even Prevent Email Messages From Being Delivered.
Overall, DNS Plays A Critical Role In The Functioning Of The Email System, And Any Issues With DNS Can Impact The Delivery And Security Of Email Messages. It's Important To Ensure That Your DNS Configuration Is Properly Set Up And Maintained To Ensure Smooth Email Function.
DNS Security Is Important For Several Reasons:
Preventing Attacks: The DNS System Is Vulnerable To Several Types Of Attacks, Including DNS Spoofing, Cache Poisoning, And DNS Hijacking, Among Others. These Attacks Can Lead To Various Malicious Activities, Such As Redirecting Users To Fake Websites, Stealing Sensitive Information, And Launching DDoS Attacks. DNS Security Measures Can Help To Prevent These Attacks And Protect Against Their Damaging Effects.
Protecting User Privacy: DNS Queries And Responses Contain Sensitive Information That Can Be Used To Track User Behavior And Compromise User Privacy. DNS Security Measures, Such As DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) And DNS-over-TLS (DoT), Can Help To Protect User Privacy By Encrypting DNS Traffic And Preventing Eavesdropping And Interception.
Ensuring Availability And Reliability: DNS Is A Critical Component Of The Internet Infrastructure, And Any Disruption Or Compromise To Its Availability And Reliability Can Have Far-reaching Consequences. DNS Security Measures, Such As DNS Filtering And DDoS Protection, Can Help To Ensure That DNS Services Are Available And Reliable Even Under Attack.
Enhancing Trust And Confidence: DNS Security Measures Can Help To Enhance The Trust And Confidence Of Users And Businesses In The Internet Infrastructure. By Demonstrating A Commitment To DNS Security And Implementing Effective Security Measures, DNS Service Providers Can Build Trust And Confidence Among Their Users And Customers.
Overall, DNS Security Is Essential For Maintaining The Integrity, Availability, And Reliability Of The DNS System, And For Protecting The Privacy And Security Of Internet Users. It Is An Ongoing Challenge That Requires Ongoing Vigilance And Protection To Stay Ahead Of Emerging Threats And Vulnerabilities.
There Are Several Common Attacks Involving DNS, Including:
DNS Spoofing Or Cache Poisoning: This Is When An Attacker Injects False DNS Data Into A DNS Resolver's Cache, Causing It To Return Incorrect Results When A User Requests A DNS Lookup. This Can Result In Users Being Redirected To Malicious Websites Or Having Their Sensitive Information Stolen.
DNS Amplification: This Is When An Attacker Sends A DNS Query To A Vulnerable DNS Server, Which Then Responds With A Much Larger Answer Than The Original Query, Causing A Distributed Denial Of Service (DDoS) Attack. The Attacker Can Then Use The Large Number Of Responses To Overwhelm The Target Network Or Server, Causing It To Become Unavailable.
DNS Hijacking: This Is When An Attacker Gains Control Of A Domain Name Or Its Authoritative DNS Server, Allowing Them To Redirect Traffic To Their Own Malicious Site. This Can Be Used For Phishing Attacks, Spreading Malware, Or Stealing Sensitive Information.
DNS Tunneling: This Is When An Attacker Uses The DNS Protocol To Bypass Network Security Measures And Exfiltrate Data From A Network. This Can Be Done By Encoding The Data In DNS Queries Or Responses, Allowing The Attacker To Evade Detection.
DNS-based Malware: This Is When Malware Uses The DNS Protocol To Communicate With Its Command-and-control (C&C) Server. This Can Be Used To Download Additional Malware, Steal Data, Or Carry Out Other Malicious Activities.
To Protect Against These Types Of Attacks, DNS Security Measures Such As DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), DNS Filtering, And Two-factor Authentication Can Be Used. It Is Also Important To Keep DNS Software And Systems Up-to-date And To Monitor DNS Traffic For Any Signs Of Suspicious Activity.
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) Is A Set Of Security Extensions To The DNS Protocol That Provides A Way To Authenticate DNS Data And Ensure Its Integrity. DNSSEC Adds Digital Signatures To DNS Records To Verify That The Data Has Not Been Tampered With And To Confirm That The Data Came From An Authoritative Source.
Without DNSSEC, DNS Data Can Be Intercepted Or Modified By Attackers, Which Can Lead To DNS Cache Poisoning And Other Attacks. DNSSEC Helps To Prevent Such Attacks By Providing A Mechanism To Verify The Authenticity Of DNS Data.
DNSSEC Operates By Using Public Key Cryptography To Sign And Verify DNS Data. Each DNS Zone Maintains A Set Of Public And Private Keys, And Digital Signatures Are Used To Verify That The Data Is Authentic And Has Not Been Tampered With. When A DNS Resolver Receives A DNS Response That Is Signed With DNSSEC, It Can Verify The Digital Signature And Confirm That The Data Is Authentic.
DNSSEC Is An Important Security Measure For DNS, And It Helps To Protect Against Various Types Of DNS Attacks, Including DNS Spoofing And Cache Poisoning. However, DNSSEC Adoption Is Not Yet Universal, And It Can Be Complex To Implement And Manage.
In Addition To DNSSEC, There Are Other Ways To Protect Against DNS-based Attacks. Here Are Some Examples:
Implement DNS Filtering: DNS Filtering Is A Method Of Blocking Or Allowing Access To Certain Websites Based On Their Domain Name. DNS Filtering Can Be Used To Block Known Malicious Domains, Preventing Users From Accessing Them And Reducing The Risk Of DNS-based Attacks.
Use Two-factor Authentication: Two-factor Authentication (2FA) Is A Security Measure That Requires Users To Provide Two Forms Of Authentication, Such As A Password And A One-time Code, To Access A System Or Service. Implementing 2FA For DNS Management Can Help To Prevent Unauthorized Access And Reduce The Risk Of DNS Hijacking.
Use Firewalls And Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Firewalls And IDS Can Help To Monitor And Block Suspicious DNS Traffic. By Monitoring DNS Queries And Responses, These Tools Can Identify Potential Attacks And Take Action To Block Or Mitigate Them.
Implement Secure DNS Servers: Ensuring That DNS Servers Are Properly Secured And Configured Is Important For Protecting Against DNS-based Attacks. This Includes Configuring Servers To Only Respond To Queries From Authorized Sources And Using Strong Passwords And Access Controls.
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regular Security Audits Can Help To Identify Vulnerabilities In DNS Systems And Processes. This Can Include Reviewing DNS Configurations, Monitoring DNS Traffic, And Testing DNS Security Measures.
By Implementing These And Other DNS Security Measures, Organizations Can Help To Protect Against DNS-based Attacks And Ensure The Integrity And Availability Of Their DNS Services.
A DNS Firewall Is A Security Tool That Is Designed To Protect Against DNS-based Attacks By Filtering DNS Traffic At The Network Level.
A DNS Firewall Works By Analyzing DNS Requests And Responses And Filtering Out Any Malicious Or Unauthorized Traffic. This Can Include Blocking Access To Known Malicious Domains, Preventing DNS Amplification Attacks, And Blocking Unauthorized DNS Traffic.
There Are Two Main Types Of DNS Firewalls: Recursive DNS Firewalls And Authoritative DNS Firewalls. Recursive DNS Firewalls Protect End Users By Filtering DNS Traffic Before It Reaches Their Devices. Authoritative DNS Firewalls Protect DNS Servers By Filtering Traffic Before It Reaches The Server.
DNS Firewalls Can Be Implemented Using Various Techniques, Including Using Blacklists And Whitelists Of Known Malicious And Legitimate Domains, And Using Machine Learning Algorithms To Detect And Block Suspicious Traffic. Some DNS Firewalls May Also Use Threat Intelligence Feeds To Identify And Block New Threats As They Emerge.
DNS Firewalls Can Be An Effective Tool For Protecting Against DNS-based Attacks, But They Should Be Used In Conjunction With Other Security Measures, Such As DNSSEC, To Provide A Comprehensive Security Strategy For DNS.
DNS Can Be Used As A Security Tool In Several Ways:
DNS Filtering: DNS Filtering Is A Technique Used To Block Or Allow Access To Certain Websites Based On Their Domain Names. DNS Filtering Can Be Used To Block Access To Known Malicious Domains, Preventing Users From Accessing Them And Reducing The Risk Of DNS-based Attacks.
DNS Sinkholing: DNS Sinkholing Is A Technique Used To Redirect Traffic From Known Malicious Domains To A Safe Location, Such As A Honeypot Or A Monitoring System. This Can Help To Detect And Mitigate Attacks, As Well As To Collect Information About The Attackers And Their Methods.
DNS-based Authentication: DNS Can Be Used As A Mechanism For Authenticating Users Or Devices. For Example, Some Organizations Use DNS-based Authentication To Verify The Identity Of Remote Users Accessing Their Network.
DNS-based Malware Detection: DNS Can Be Used To Detect And Block Malware By Identifying And Blocking Requests To Known Malicious Domains. This Can Help To Prevent Malware From Entering The Network And Spreading To Other Devices.
DNS-based Threat Intelligence: DNS Can Be Used As A Source Of Threat Intelligence, Providing Information About The Domains And IP Addresses Associated With Known Threats. This Information Can Be Used To Block Access To Malicious Domains And To Identify Potential Threats Before They Become Active.
DNS Can Be A Valuable Security Tool When Used In Conjunction With Other Security Measures, Such As Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems, And Endpoint Protection. By Leveraging The Capabilities Of DNS, Organizations Can Improve Their Security Posture And Better Protect Their Networks And Devices From Threats.